Food additives: tartaric acid and tartrates
- Food additives
- Food safety
Summary
The EU has revised conditions of use for the food additives tartaric acid (E 334), sodium tartrates (E 335), potassium tartrates (E 336), sodium potassium tartrate (E 337), and calcium tartrate (E 354) in several food categories. For certain food categories where the food industry did not express interest in the use of tartaric acid or tartrates, authorisation has been withdrawn and their use will no longer be permitted.
EU reviews authorisations of tartaric acid and tartrates (E 334–337 and E 354), and sets maximum use levels
Commission Regulation (EU) 2024/1451 of 24 May 2024 amending Annex II and Annex III to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the food additives tartaric acid (L(+)-) (E 334), sodium tartrates (E 335), potassium tartrates (E 336), sodium potassium tartrate (E 337) and calcium tartrate (E 354)
Update
The EU has revised conditions of use for the food additives tartaric acid (E 334), sodium tartrates (E 335), potassium tartrates (E 336), sodium potassium tartrate (E 337), and calcium tartrate (E 354) in several food categories. For certain food categories where the food industry did not express interest in the use of tartaric acid or tartrates, authorisation has been withdrawn and their use will no longer be permitted.
Impacted Products
Processed foods including baked goods, beverages, confectionery, desserts and jellies, heat-treated meat products, processed fruits, vegetables, and dairy products, processed fish and fishery products (including molluscs and crustaceans), table-top sweeteners, seasonings, condiments
What is changing?
Before this Regulation, tartaric acid and tartrates (E 334–337 and E 354) were included in Group I of Regulation 1333/2008 “food additives other than colours and sweeteners without a specified acceptable daily intake (ADI)”. Following a re-evaluation of these additives, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) established a group ADI for these additives (E 334–337 and E 354) of 240 mg/kg body weight per day, expressed as tartaric acid (EFSA 2020). They are removed from Group I and placed in a new group (tartaric acid – tartrates).
This Regulation establishes conditions of use for these food additives and withdraws their authorisations in certain food categories (see Table 1 for details).
The Regulation also establishes conditions of use of tartaric acid and tartrates in food additives, food enzymes, and food flavourings. These conditions are set out in Annex II.
Why?
Food additives used in processed foods are reassessed regularly to ensure their safe use in food products.
Following EFSA’s review of tartaric acid and tartrates and establishment of a group ADI (EFSA 2020), the European Commission launched a public call for technical data on the use of these food additives. Where no data were provided in relation to a specific food category or use, the Commission considered that there was no interest in reauthorisation, and the authorisation has been withdrawn.
Timeline
Date of application: 16 December 2024.
Foods containing these additives may remain on the market until their date of minimum durability or use-by date, even if they do not comply with the new rules, provided they have been lawfully placed on the market before 16 December 2024.
What are the major implications for exporting countries?
Exporting countries must ensure that their food products meet the latest EU standards for food additives. This means adhering to the specific additives listed in Annexes II and III of Regulation 1333/2008, and their allowed quantities. Failure to comply could result in entry into the EU market being refused.
Recommended Actions
Suppliers of foods containing tartaric acid and tartrates must comply with the new maximum levels for each food category, and ensure that these additives are not used in food categories for which their use is no longer authorised.
Background
Regulation 1333/2008 outlines the rules for assessment and approval of food additives within the European Union.
- List of Approved Food Additives (Annex II) specifies which food additives are allowed to be used in various categories of food products. Only the additives listed here are permitted for use, and they must be used according to the specified conditions.
- List for Specific Applications (Annex III) details which food additives can be used in the manufacturing of other food additives, enzymes, and flavourings. Additives must be used as outlined in this list to comply with the Regulation.
This Regulation also specifies the maximum amounts that can be used in food products. These limits are based on two main principles:
- minimal necessary quantity: additives should be used in the smallest quantity needed to achieve their intended function, such as food preservation or flavour enhancement
- safety considerations: the quantities used must ensure safety for all consumer groups and reflect the ADI levels, particularly for populations with potentially higher consumption.
For the most recently updated list of approved food additives and conditions of use, see Regulation 1333/2008: click on the date that follows “Current consolidated version”.
Resources
EFSA (2020) Re-evaluation of l(+)-tartaric acid (E 334), sodium tartrates (E 335), potassium tartrates (E 336), potassium sodium tartrate (E 337) and calcium tartrate (E 354) as food additives. EFSA Journal, 18(3): 6030.
Online resources from the European Commission:
Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 on food additives
Sources
Commission Regulation (EU) 2024/1451 as regards the food additives tartaric acid (L(+)-) (E 334), sodium tartrates (E 335), potassium tartrates (E 336), sodium potassium tartrate (E 337) and calcium tartrate (E 354)
Tables & Figures
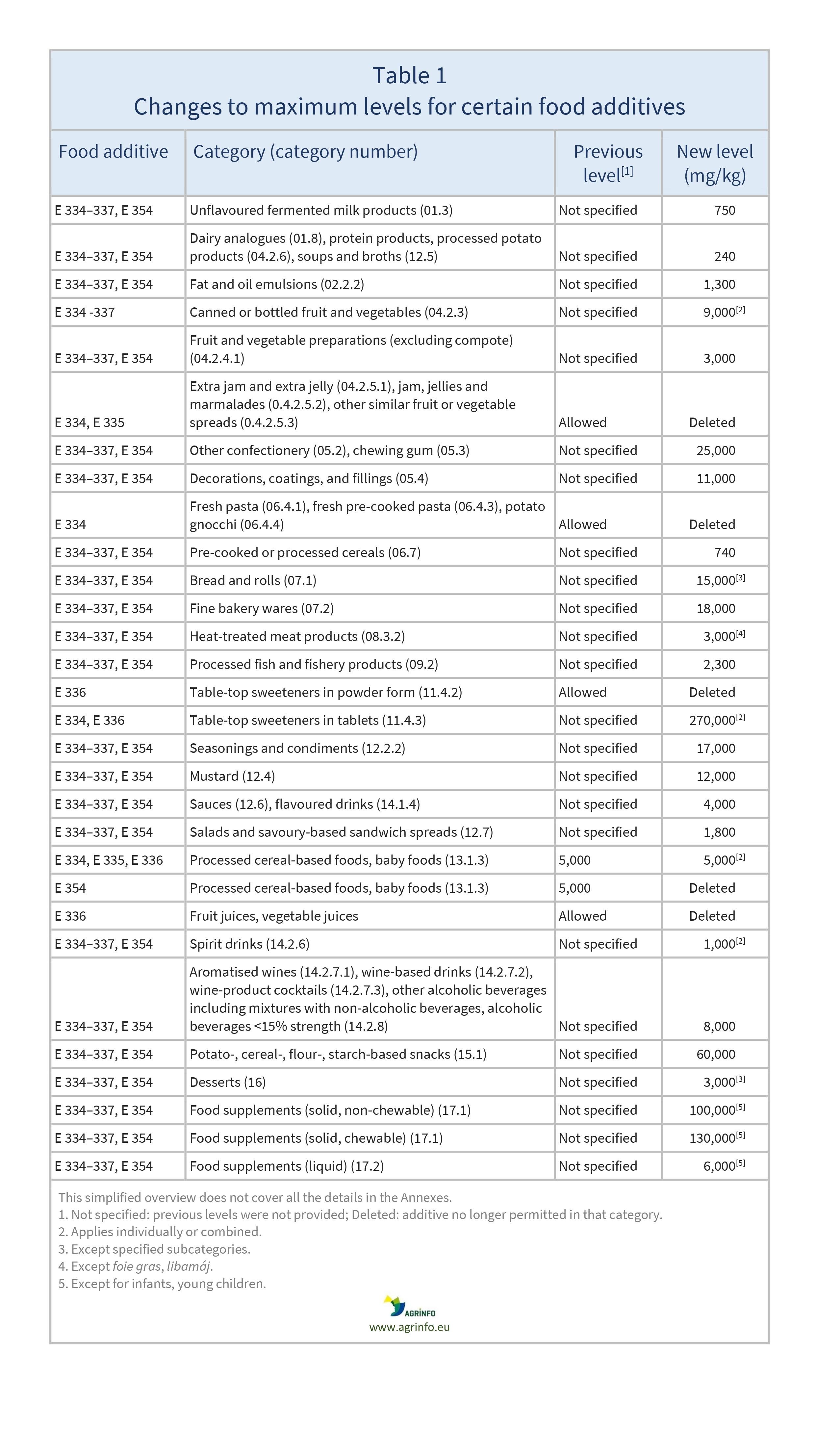
Source: Regulation 2024/1451, Annex I
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
EU reviews authorisations of tartaric acid and tartrates (E 334–337 and E 354), and sets maximum use levels
Commission Regulation (EU) 2024/1451 as regards the food additives tartaric acid (L(+)-) (E 334), sodium tartrates (E 335), potassium tartrates (E 336), sodium potassium tartrate (E 337) and calcium tartrate (E 354)
What is changing and why?
The EU has introduced conditions of use for tartaric acid and tartrates (E 334–337 and E 354) in many food categories (see Table 1 for details). This is because, after consulting food businesses, the European Food Safety Authority has re-evaluated these additives and established an acceptable daily intake level for this group. Where food businesses provided no technical data to support reauthorisation for a specific food category or use, the Commission considered that there was no interest, and the authorisation has been withdrawn.
Actions
Suppliers of foods containing tartaric acid and tartrates (E 334–337 and E 354) must comply with the new maximum levels set for each food category, and ensure that these additives are not used in food categories for which their use is no longer authorised.
Timeline
Date of application: 16 December 2024.
Foods containing these additives may remain on the market until their date of minimum durability or use-by date, even if they do not comply with the new rules, provided they have been lawfully placed on the market before 16 December 2024.
Tables & Figures

Source: Regulation 2024/1451, Annex I
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
