Feed additives: March–April 2024 authorisations
- Feed additives
- Feed safety
Summary
An overview of the latest authorisations and reauthorisations of feed additives and their use in animal nutrition in target animals.
EU authorises or reauthorises certain feed additives
Commission Implementing Regulations 2024/764, 2024/771, 2024/777, 2024/778, 2024/780, 2024/781, 2024/786, 2024/794, 2024/806, 2024/824, 2024/997, 2024/1054, 2024/1055, 2024/1056, 2024/1057, 2024/1058, 2024/1070, 2024/1104, 2024/1161, 2024/1179, 2024/1185, 2024/1186, 2024/1187, 2024/1189, 2024/1190, 2024/1194, 2024/1195, 2024/1196, 2024/1199, 2024/1200
Update
An overview of the latest authorisations and reauthorisations of feed additives and their use in animal nutrition in target animals.
Impacted Products
Feed additives, prepared fodder
What is changing?
New authorisations
In March and April 2024, the EU authorised the new feed additives listed in Table 1.
These authorisations are based on opinions published by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) [see Resources 1–21].
Reauthorisations
In March and April 2024, the EU reauthorised the feed additives listed in Table 2, based on opinions published by EFSA [see Resources 14, 16, 21, 22–31].
Amended authorisations
Regulation 2024/1054 authorises the use of a preparation of Weizmannia faecalis DSM 32016 for suckling and weaned piglets, poultry for fattening, and ornamental birds, together with some other antiprotozoal agents. EFSA’s opinion [20] states which of these uses are compatible, which are not, and for which uses no conclusions could be drawn about compatibility.
Regulation 2024/771 amends Regulation 152/2009 laying down the methods of sampling and analysis for the official control of feed.
Withdrawals
The following will be withdrawn from the market for animal species and categories other than those mentioned in the Regulation's Annex:
- Regulation 2024/1186: Cinnamon bark essential oil and cinnamon leaf essential oil from Cinnamomum verum
- Regulation 2024/1195: Cassia essential oil from Cinnamomum aromaticum.
Why?
Applications for the above authorisations and reauthorisations were submitted and considered by the Reference Laboratory set up by the Feed Additives Regulation (1831/2003).
Timeline
New authorisations remain valid until the end dates listed in Table 1.
Reauthorisations remain valid until the end dates listed in Table 2.
What are the major implications for exporting countries?
With new authorisations, more feed additives will be available on the market. Authorisations and renewals are valid for 10 years. The use of all preparations and substances specified as feed additives must comply with the provisions specified in the Annex to each Regulation.
Recommended Actions
Non-EU countries producing feed additives, compound feed, and feed materials for export to the EU are recommended to check the status of the feed additives in the EU Feed Additives register.
To be able to filter and to see more information, it is advised to download the register in Excel format (see foot of Food and Feed Information Portal).
Background
The procedure for authorising the placing on the market and use of feed additives is set out in Regulation (EC) 1831/2003. For the latest updates on feed additives see the EU Feed Additives register.
Resources
Opinions published by the European Food Safety Authority on the safety/efficacy of the following feed additives
- An essential oil from Cinnamomum cassia (cassia leaf oil). EFSA Journal, 20(10): 7600.
- Essential oils from the bark and the leaves of Cinnamomum verum (cinnamon bark oil and cinnamon leaf oil). EFSA Journal, 20(10): 7601.
- Riboflavin‐5′‐phosphate ester monosodium salt (vitamin B2) (from riboflavin 98%, produced by Bacillus subtilisKCCM 10445). EFSA Journal, 20(11): 7608.
- A tincture derived from the roots of Gentiana lutea (gentian tincture). EFSA Journal, 21(2): 7869.
- Bacillus subtilis strains CNCM I-4606, CNCM I-5043 and CNCM I-4607 and Lactococcus lactis CNCM I-4609. EFSA Journal, 21(3): 7871.
- A preparation of essential oils of thyme and star anise, and quillaja bark powder (BIOSTRONG® 510 all natural). EFSA Journal, 21(4): 7955.
- Lactiplantibacillus plantarum DSM 11520. EFSA Journal, 21(4): 7974.
- Concentrated liquid l-lysine, l-lysine monohydrochloride and concentrated liquid l-lysine monohydrochloride produced by Escherichia coli NITE BP-02917. EFSA Journal, 21(6): 8048.
- l‐valine produced by Corynebacterium glutamicum CGMCC 18932. EFSA Journal, 21(7): 8104.
- A tincture derived from the buds of Pinus sylvestris (pine tincture). EFSA Journal, 21(7): 8181.
- Endo-β-1,4-xylanase produced by Komagataella phaffii CGMCC 7.371 (VTR-xylanase). EFSA Journal, 21(8): 8150.
- Protease produced by Bacillus licheniformis DSM 33099 (ProAct 360). EFSA Journal, 21(8): 8163.
- 25-hydroxycholecalciferol monohydrate produced with Saccharomyces cerevisiae CBS 146008. EFSA Journal, 21(8): 8169.
- Endo-1,4-β-xylanase produced by Trichoderma citrinoviride DSM 34663 (Hostazym® X). EFSA Journal, 21(8): 8171.
- Iron(II)‐betaine complex. EFSA Journal, 21(9): 8250.
- Endo‐1,4‐beta‐xylanase (produced by Aspergillus oryzae DSM 33700). EFSA Journal, 21(10): 8339.
- 6‐phytase (produced by Komagataella phaffii CGMCC 7.19) (Nutrase P). EFSA Journal, 21(10): 8345.
- Enterococcus lactis NCIMB 10415 (Cylactin®). EFSA Journal, 21(10): 8347.
- Manganese(II)-betaine complex. EFSA Journal, 21(10): 8362.
- Weizmannia faecalis DSM 32016 (TechnoSpore50®). EFSA Journal, 21(11): 8355.
- Enterococcus faecium DSM 21913, Bifidobacterium animalis DSM 16284 and Ligilactobacillus salivarius DSM 16351 (Biomin® C3). EFSA Journal, 21(12): 8356.
- Lactiplantibacillus plantarum DSM 3676, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum DSM 3677 and Lentilactobacillus buchneriDSM 13573. EFSA Journal, 21(7): 8162.
- 25-hydroxycholecalciferol produced with Saccharomyces cerevisiae CBS 146008. EFSA Journal, 21(8): 8168.
- Alpha-galactosidase produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae CBS 615.94 and endo-1,4-beta-glucanase produced by Aspergillus niger CBS 120604 (Agal-Pro BL/BL-L®). EFSA Journal, 21(8): 8175.
- Lactiplantibacillus plantarum LMG P-21295. EFSA Journal, 21(10): 8346.
- Enterococcus lactis DSM 7134 and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus DSM 7133 (Provita LE). EFSA Journal, 21(10): 8350.
- Enterococcus lactis DSM 7134 (Bonvital®). EFSA Journal, 21(10): 8351.
- Lentilactobacillus buchneri DSM 19455. EFSA Journal, 21(10): 8352.
- Niacinamide. EFSA Journal, 21(10): 8357.
- Niacin (nicotinic acid). EFSA Journal, 21(10): 8359.
- Orthophosphoric acid. EFSA Journal, 21(10): 8361.
Sources
Regulations 2024/764, 2024/771, 2024/777, 2024/778, 2024/780, 2024/781, 2024/786, 2024/794, 2024/806, 2024/824, 2024/997, 2024/1054, 2024/1055, 2024/1056, 2024/1057, 2024/1058, 2024/1070, 2024/1104, 2024/1161, 2024/1179, 2024/1185, 2024/1186, 2024/1187, 2024/1189, 2024/1190, 2024/1194, 2024/1195, 2024/1196, 2024/1199, 2024/1200
Regulation 1831/2003 on additives for use in animal nutrition
Tables & Figures
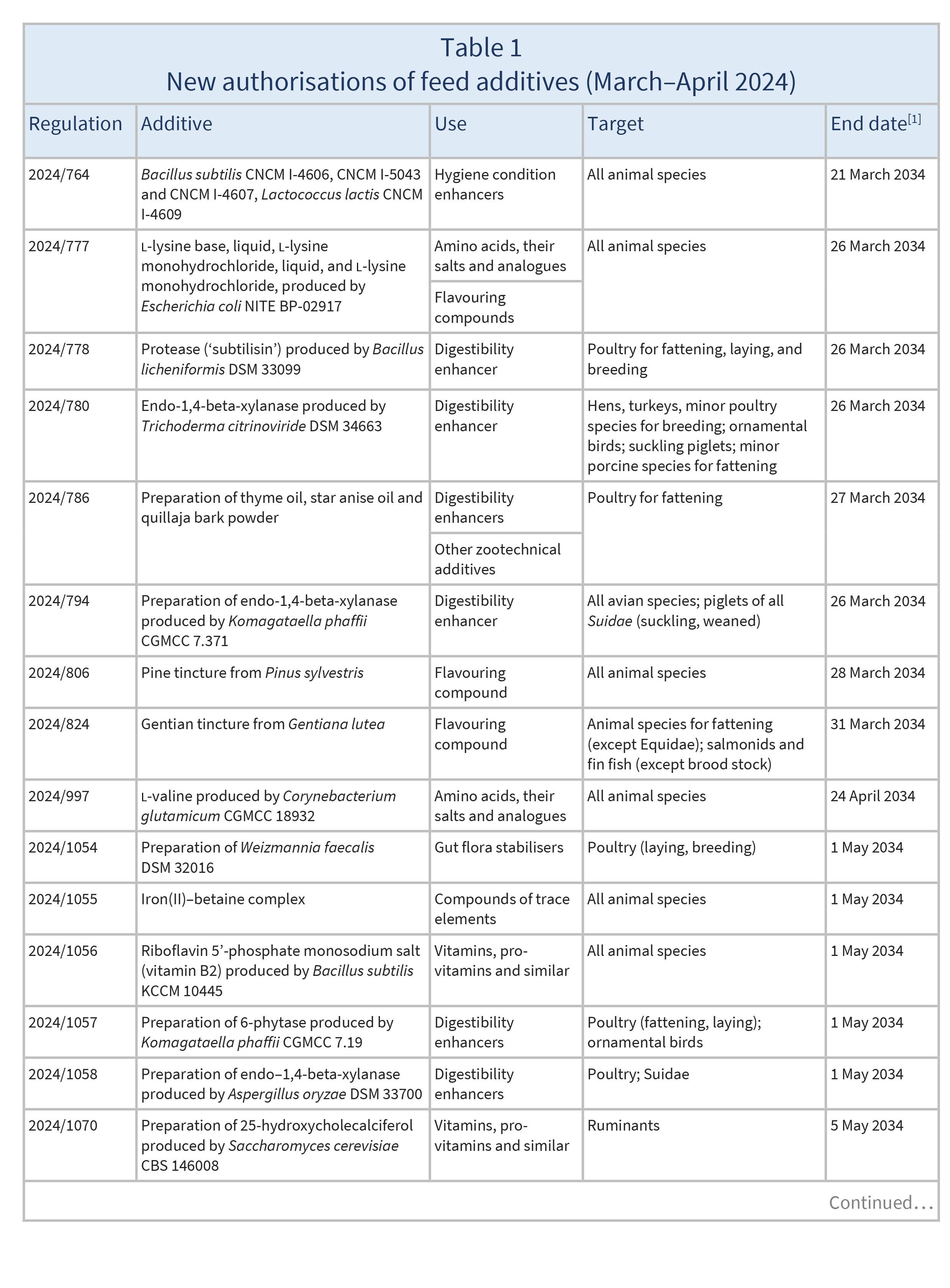
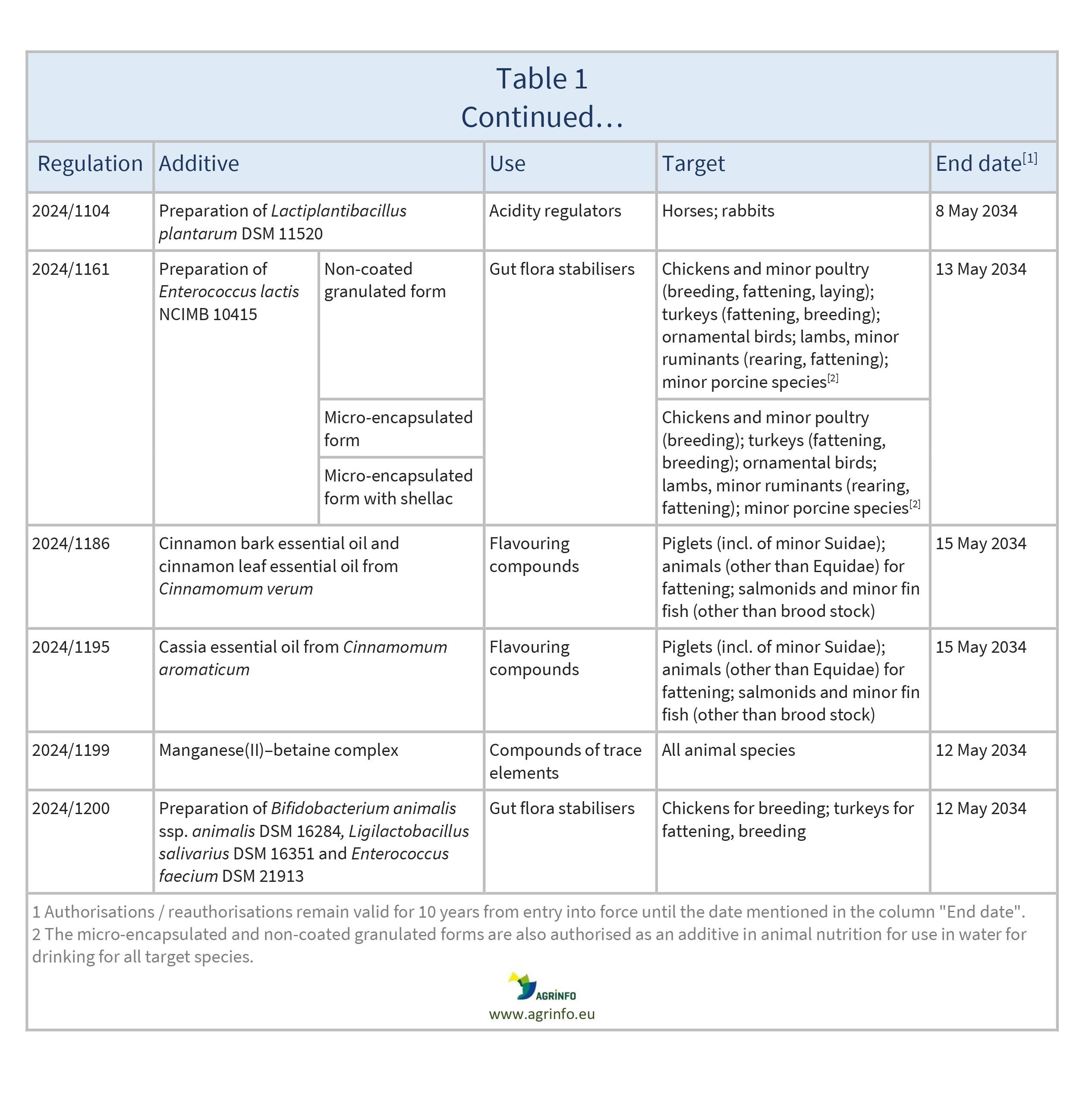
Source: based on Regulations 2024/764, 2024/777, 2024/778, 2024/780, 2024/786, 2024/794, 2024/806, 2024/824, 2024/997, 2024/1054, 2024/1055, 2024/1056, 2024/1057, 2024/1058, 2024/1070, 2024/1104, 2024/1161, 2024/1186, 2024/1195, 2024/1199, 2024/1200
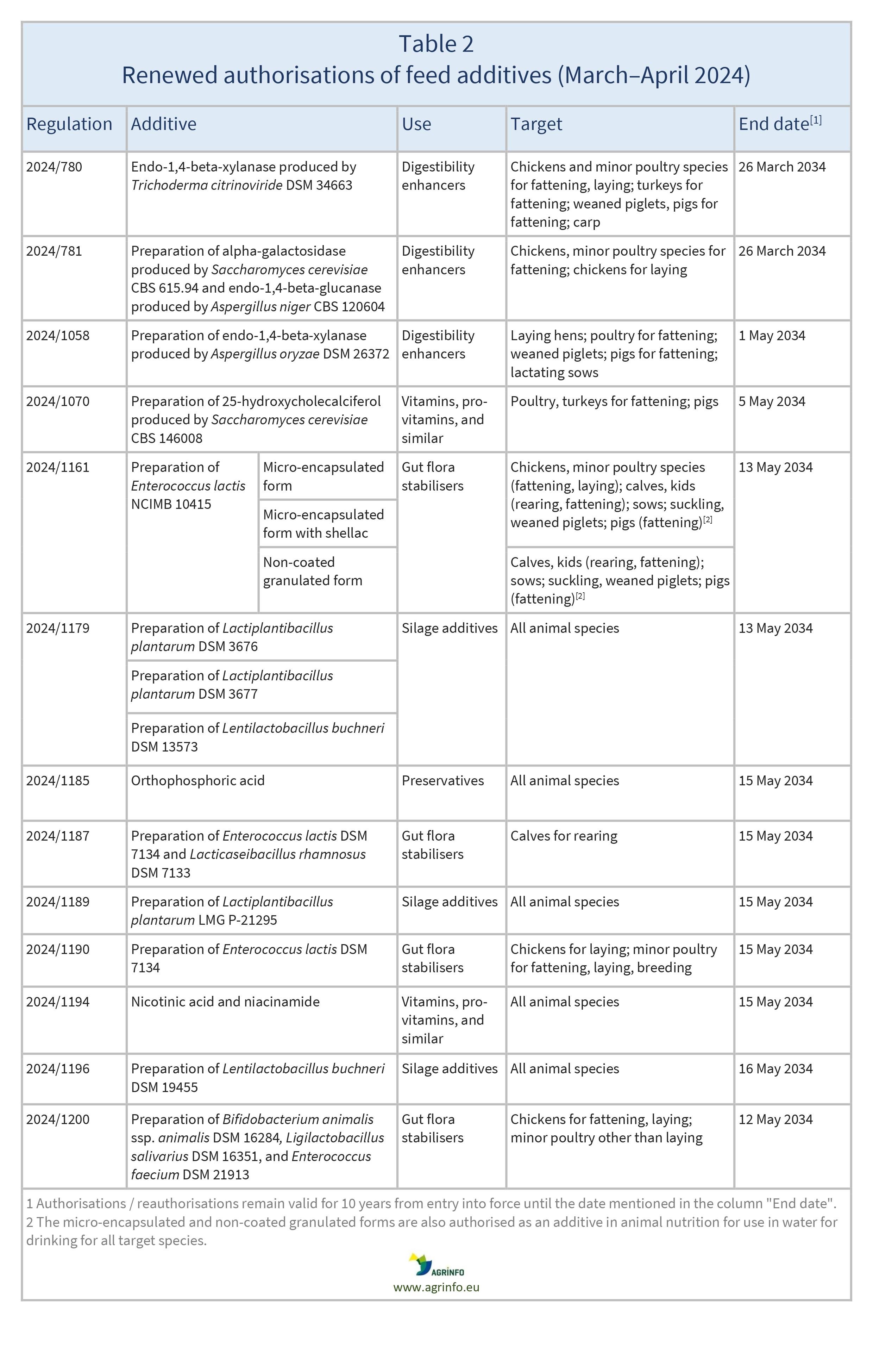
Source: based on Regulations 2024/780, 2024/781, 2024/1058, 2024/1070, 2024/1161, 2024/1179, 2024/1185, 2024/1187, 2024/1189, 2024/1190, 2024/1194, 2024/1196, 2024/1200
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
EU authorises or reauthorises certain feed additives
Regulations 2024/764, 2024/771, 2024/777, 2024/778, 2024/780, 2024/781, 2024/786, 2024/794, 2024/806, 2024/824, 2024/997, 2024/1054, 2024/1055, 2024/1056, 2024/1057, 2024/1058, 2024/1070, 2024/1104, 2024/1161, 2024/1179, 2024/1185, 2024/1186, 2024/1187, 2024/1189, 2024/1190, 2024/1194, 2024/1195, 2024/1196, 2024/1199, 2024/1200
What is changing and why?
In March and April 2024, the EU authorised the new feed additives listed in Table 1. Applications for these authorisations were submitted and considered by the Reference Laboratory set up by the Feed Additives Regulation (1831/2003).
The EU has reauthorised the feed additives listed in Table 2.
The EU has also authorised the use of a preparation of Weizmannia faecalis DSM 32016 for suckling and weaned piglets, poultry for fattening, and ornamental birds, together with some other antiprotozoal agents, because the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) considers that these uses are compatible (Regulation 2024/1054).
Regulation 2024/771 amends Regulation 152/2009 laying down the methods of sampling and analysis for the official control of feed.
Actions
Non-EU countries producing feed additives, compound feed, and feed materials for export to the EU are recommended to check the status of feed additives in the EU Feed Additives register.
To be able to filter and to see more information, it is advised to download the register in Excel format (see foot of Food and Feed Information Portal).
Timeline
New authorisations are valid until the end dates listed in Table 1.
Reauthorisations are valid until the end dates listed in Table 2.
Tables & Figures


Source: based on Regulations 2024/764, 2024/777, 2024/778, 2024/780, 2024/786, 2024/794, 2024/806, 2024/824, 2024/997, 2024/1054, 2024/1055, 2024/1056, 2024/1057, 2024/1058, 2024/1070, 2024/1104, 2024/1161, 2024/1186, 2024/1195, 2024/1199, 2024/1200

Source: based on Regulations 2024/780, 2024/781, 2024/1058, 2024/1070, 2024/1161, 2024/1179, 2024/1185, 2024/1187, 2024/1189, 2024/1190, 2024/1194, 2024/1196, 2024/1200
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
