Foods subject to controls of radioactive contamination related to Chernobyl
- Contaminants
- Food safety
- Food safety controls
- Official controls
Summary
Countries affected by the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear power station accident must fulfil certain requirements when exporting wild mushrooms and Vaccinium fruits to the EU (Regulation 2020/1158). The EU has now extended the list of foods affected to include processed products containing wild mushrooms and fruits of the genus Vaccinium. This affects exporters of these products in Albania, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Moldova, Montenegro, Russia, Serbia, Switzerland, Türkiye, Ukraine, and United Kingdom excluding Northern Ireland (Great Britain).
EU extends list of foods to be controlled for radioactive contamination
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2024/256 of 17 January 2024 amending Implementing Regulation (EU) 2020/1158 on the conditions governing imports of food and feed originating in third countries following the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power station
Update
Countries affected by the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear power station accident must fulfil certain requirements when exporting wild mushrooms and Vaccinium fruits to the EU (Regulation 2020/1158). The EU has now extended the list of foods affected to include processed products containing wild mushrooms and fruits of the genus Vaccinium. This affects exporters of these products in Albania, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Moldova, Montenegro, Russia, Serbia, Switzerland, Türkiye, Ukraine, and United Kingdom excluding Northern Ireland (Great Britain).
Impacted Products
Mushrooms, fruits, nuts, juices, waters, sugar confectionery, chocolate, bakery wares
What is changing?
Certain foods and food products exported to the EU from countries impacted by the Chernobyl accident must be accompanied by certificates demonstrating that they are free from radioactive contamination. This new Regulation amends the list of impacted products, as shown in Table 1.
For a full list of impacted foods (with CN customs codes) see the Annex to Regulation 2024/256.
The new Regulation also:
- specifies that for concentrated or dried products the maximum level is to be calculated on the reconstituted product as ready for consumption (footnote added to Art. 3)
- updates the legal references to the model official certificates (Regulation 2019/628 is replaced by Regulation 2020/2235 in Arts. 4.3 and 4.4)
- specifies that controls on products containing ingredients of animal origin must be performed at a border control post (rather than a designated control point or border control post in the case of non-animal products).
Why?
The scope of Regulation 2020/1158 needs to be expanded to a wider range of products to ensure consumers are adequately protected from risks of radioactive contamination related to the Chernobyl nuclear power station accident.
Timeline
Date of application: 7 February 2024.
Products that are new to the list (mixtures and processed foods containing wild mushrooms/wild fruits of the genus Vaccinium) that were produced before 7 February 2024 can enter the EU without mandatory certificates until 7 March 2024.
Recommended Actions
Exporters in the listed countries of mixtures and processed products containing wild mushrooms or wild Vaccinium fruits should urgently check whether they are affected by this revised list of products. Exporters of affected products must ensure compliance with maximum levels of radioactivity, and must obtain official certificates from their competent authorities prior to export.
Businesses and competent authorities in the affected exporting countries must expand controls of radioactive contamination in wild mushrooms and Vaccinium fruits to mixtures and processed foods that contain these mushrooms/fruits.
Background
Regulation 2020/1158 was adopted in relation to the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power station on 26 April 1986 in order to assess the safety of food and feed imported from the following countries affected by the accident: Albania, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Moldova, Montenegro, Russia, Serbia, Switzerland, Türkiye, Ukraine, and United Kingdom excluding Northern Ireland (Great Britain).
The Regulation lays down maximum permitted levels of radioactive contamination in terms of caesium-137:
- for milk and milk products, and for food for infants and young children [Regulation 609/2013, Art. 2(2)(a,b)]: 370 Bq/kg
- for all other products concerned: 600 Bq/kg.
A list of the products that must be accompanied by an official certificate when entering the EU is given in Regulation 2020/1158 (Annex II, Art. 4).
Competent authorities of border control posts where products enter the EU must carry out identity checks and physical checks on these consignments.
Resources
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2020/1158 on the conditions governing imports of food and feed originating in third countries following the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power station
Sources
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2024/256 on the conditions governing imports of food and feed originating in third countries following the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power station
Tables & Figures
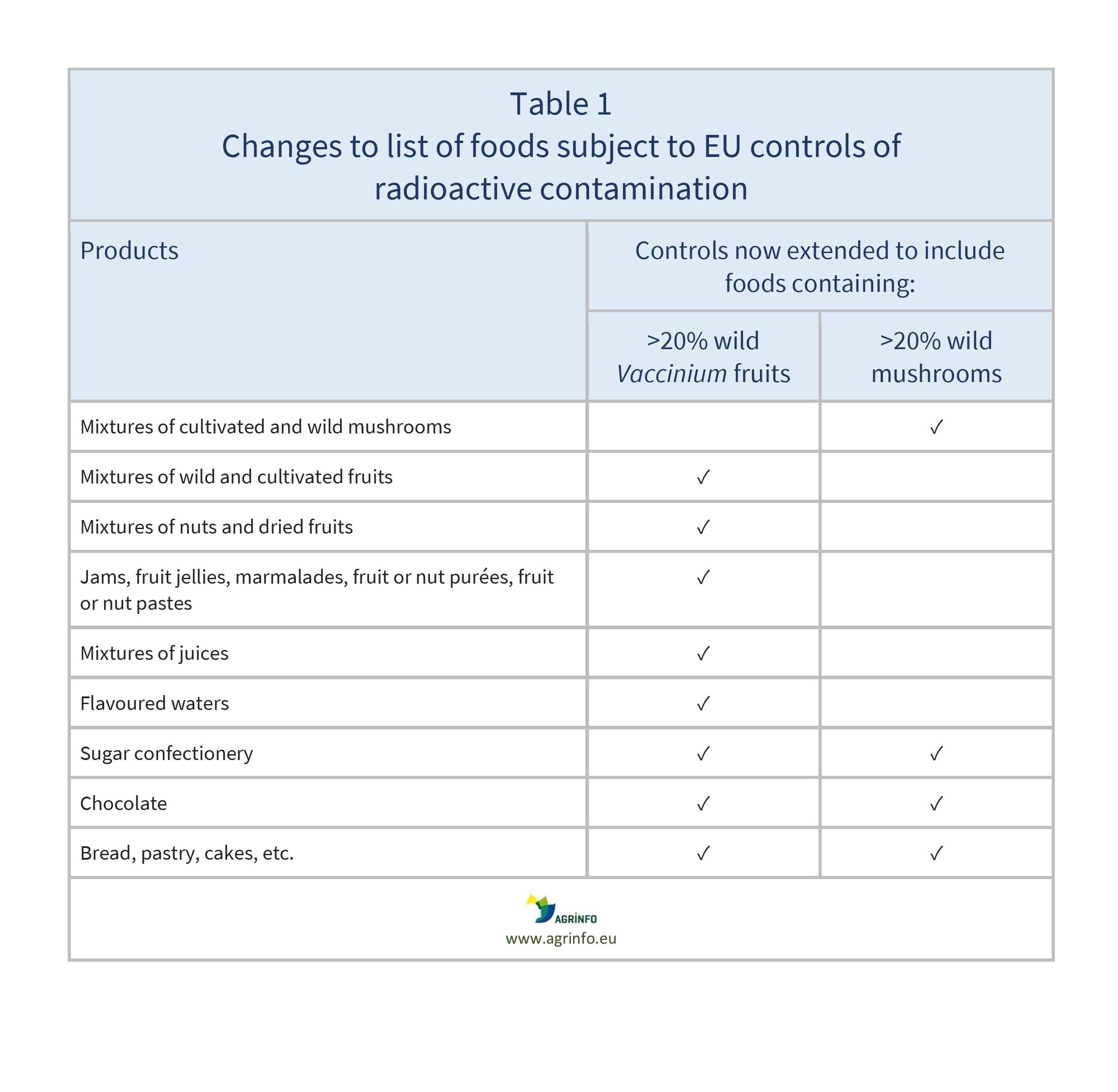
Source: based on Regulation (EU) 2024/256 (Annex)
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
EU extends list of foods to be controlled for radioactive contamination
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2024/256 on the conditions governing imports of food and feed originating in third countries following the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power station
What is changing and why?
Certain foods and food products exported to the EU from countries impacted by the Chernobyl accident must be accompanied by certificates demonstrating that they are free from radioactive contamination.
This new Regulation amends the list of impacted products, as shown in Table 1.
The affected countries are: Albania, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Moldova, Montenegro, Russia, Serbia, Switzerland, Türkiye, Ukraine, and UK excluding Northern Ireland (Great Britain).
These changes are intended to protect EU consumers from potential risks of radioactive contamination.
Actions
Exporters of products containing wild mushrooms or wild Vaccinium fruits should urgently check whether they are affected by this revised list of products. Exporters of affected products must ensure compliance with maximum levels of radioactivity, and must obtain official certificates from their competent authorities prior to export.
Businesses and competent authorities in the affected exporting countries must expand controls of radioactive contamination in wild mushrooms and Vaccinium fruits to mixtures and processed foods that contain these mushrooms/fruits.
Timeline
Date of application: 7 February 2024.
Products that are new to the list (mixtures and processed foods containing wild mushrooms/wild fruits of the genus Vaccinium) that were produced before 7 February 2024 can enter the EU without mandatory certificates until 7 March 2024.
Tables & Figures

Source: based on Regulation (EU) 2024/256 (Annex)
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
