Maximum residue levels for acequinocyl
- Pesticide MRLs
Summary
On 2 August 2022, the EU published a Regulation increasing MRLs for acequinocyl on specific fruit and vegetables, and reducing the MRL on almonds to the limit of determination (LOD).
On 19 January 2023, the EU published a Regulation increasing MRLs for acequinocyl on kaki/ Japanese persimmons and sweet peppers/ bell peppers.
EU increases MRLs for acequinocyl on specific fruits and vegetables, and reduces the MRL on almonds to the limit of determination
Commission Regulation (EU) 2022/1343 of 29 July 2022 amending Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards maximum residue levels for acequinocyl, chlorantraniliprole and emamectin in or on certain products
Commission Regulation (EU) 2023/127 of 18 January 2023 amending Annex II to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards maximum residue levels for acequinocyl in or on certain products
Update
On 2 August 2022, the EU published a Regulation increasing MRLs for acequinocyl on specific fruit and vegetables, and reducing the MRL on almonds to the limit of determination (LOD).
On 19 January 2023, the EU published a Regulation increasing MRLs for acequinocyl on kaki/ Japanese persimmons and sweet peppers/ bell peppers.
Impacted Products
almonds, apples, pears, quinces, medlars, loquats, Japanese medlars, peaches, plums, table grapes, wine grapes, tomatoes, aubergines, eggplants, courgettes, kaki, Japanese persimmons, sweet peppers, bell peppers
What is changing?
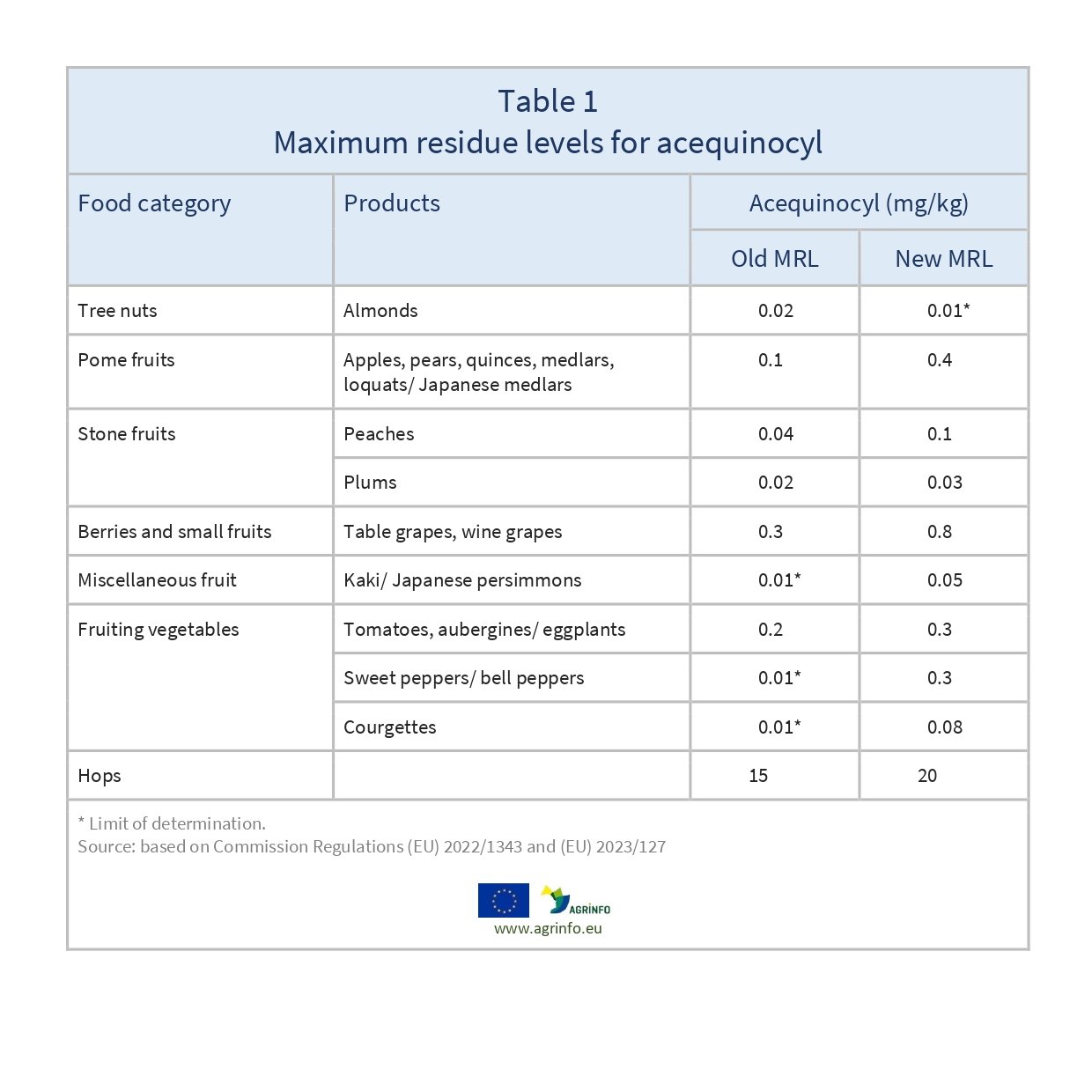
The EU amended MRLs for acequinocyl as set out in Table 1.
In addition, the LOD on herbs and edible flowers is increased from 0.01 to 0.02 mg/kg, and for teas, coffee, herbal infusions and spices is increased from 0.02 to 0.05 mg/kg.
Why?
Following its review of existing acequinocyl MRLs, EFSA (2020) recommended raising or keeping the vast majority of existing MRLs. Due to insufficient information on various products, these MRLs will be reviewed by July 2024.
A subsequent application for an MRL on sweet peppers/ bell peppers and kaki/ Japanese persimmons was submitted and accepted. EFSA (2022) concluded that short-term and long-term intake of residues on peppers resulting from agricultural practice is unlikely to present a risk to consumer health. For kaki/ Japanese persimmons, consumer safety could be confirmed through extrapolation from pesticide residue trials.
Timeline
The new MRLs apply from 22 February 2023. For products imported into the EU before that date and remaining on the market after that date, the old MRLs will apply.
The new MRLs on kaki and bell peppers/ sweet peppers apply from 23 February 2023.
Recommended Actions
Suppliers of almonds should review current use of acequinocyl with a view to seeking alternative solutions before February 2023.
Background
MRLs are set in accordance with the rules set out in Regulation 396/2005. For information on current MRLs for other substances, please consult the EU Pesticide Residues database.
Resources
EFSA (2020) Review of the existing maximum residue levels for acequinocyl according to Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 396/2005.EFSA Journal, 18(1): 5983.
EFSA (2022) Modification of the existing maximum residue level for acequinocyl in sweet peppers/bell peppers. EFSA Journal, 20(3): e07175.
Sources
Tables & Figures
.
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
