Maximum residue levels for copper compounds
- Food safety
- Pesticide MRLs
Summary
The European Union (EU) will raise the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for copper compounds on a wide range of products.
The European Commission initially proposed to reduce the MRLs on certain other products. However, this has been postponed to allow more opportunity to collect and review data for those products.
EU to raise MRLs for copper compounds on certain foods
Draft Commission Regulation amending Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards maximum residue levels for copper compounds in or on certain products
Draft Annex II (PLAN/2025/350 draft v3)
Update
The European Union (EU) will raise the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for copper compounds on a wide range of products.
The European Commission initially proposed to reduce the MRLs on certain other products. However, this has been postponed to allow more opportunity to collect and review data for those products.
Impacted Products
Almonds, Brazil nuts, chestnuts, hazelnuts, macadamias, pecans, pine nut kernels, pistachios, walnuts, apples, pears, quinces, medlars, loquats/Japanese medlars, cherries, peaches, table grapes, wine grapes, strawberries, blueberries, cranberries, currants (black, red, white), gooseberries (green, red, yellow), rose hips, mulberries (black and white), azaroles/Mediterranean medlars, elderberries, kiwi fruits (green, red, yellow), potatoes, horseradishes, spring onions/green onions, Welsh onions, tomatoes, aubergines/eggplants, sweet peppers/bell peppers, melons, pumpkins, watermelons, Chinese cabbages/pe-tsai, kales, lamb’s lettuces, lettuces, escaroles, cresses and other sprouts and shoots, land cresses, Roman rocket/rucola, red mustards, baby leaf crops, spinaches, purslanes, chards/beet leaves, watercresses, chervil, chives, parsley, sage, rosemary, thyme, basil and edible flowers, laurel/bay leaves, tarragon, grape leaves and similar species, celery leaves, leeks, globe artichokes, buckwheat, sorghum, hops, liver (swine, cattle, sheep, goat, other farmed terrestrial animals), muscle (goat), honey and other apiculture products, amphibians and reptiles, terrestrial vertebrate animals, wild terrestrial invertebrate animals
What is changing?
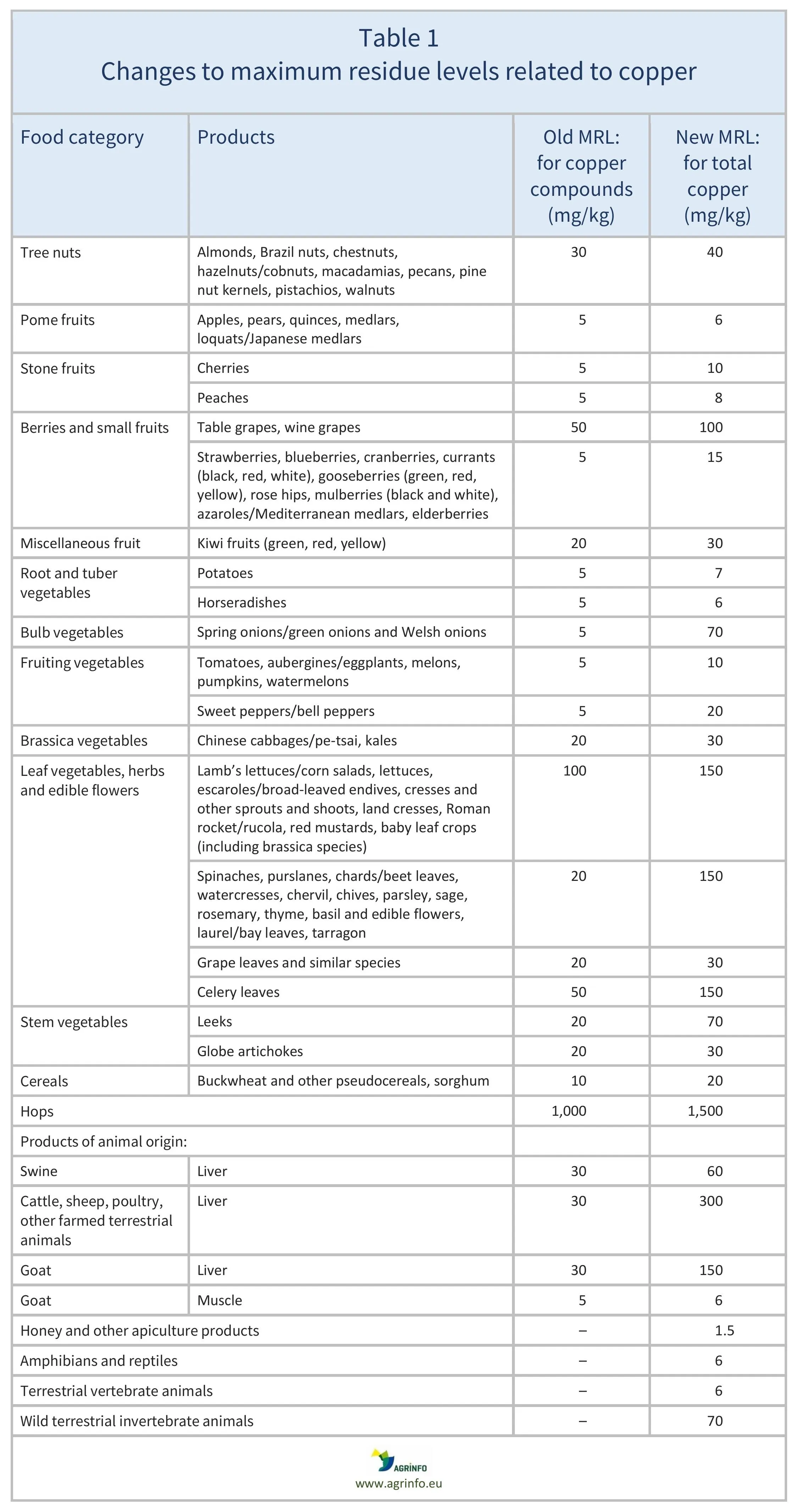
The EU is amending the MRLs for copper compounds on certain products, as summarised in Table 1.
The European Commission initially proposed to lower the MRLs on certain other products, but this has been postponed to allow stakeholders to submit monitoring data to the European Food Safety Authority for evaluation (European Commission 2025).
The residue definition will be changed from “copper compounds (copper)” to “total copper”.
Why?
The changes are based on updated scientific assessments by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA 2025), which reviewed all sources of exposure and considered both authorised uses of copper as a pesticide and the widespread natural presence of copper in soil and water.
Timeline
The Regulation is expected to be published and to apply from April 2026.
Recommended Actions
EFSA collects a wide range of chemical data on an annual basis. The process of MRL setting is influenced by the scope and representativity of the monitoring data available to EFSA to conduct their analysis. It is therefore in the interest of operators in non-EU countries to work with partners and counterparts in the EU to submit data as part of the annual monitoring of chemical data (European Commission 2025). Data must be submitted by European partners in the specific format required by EFSA. For further information on how to submit data, see EFSA (2020, 2026).
Background
MRLs are set in accordance with the rules set out in Regulation 396/2005. For information on current MRLs for other substances, please consult the EU Pesticide Residues database.
Resources
EFSA (2020) Sending data to EFSA – a short guide [video].
EFSA (2025) Statement on the update of maximum residue levels (MRLs) for copper compounds in light of the EFSA scientific opinion on the re‐evaluation of the health‐based guidance values (HBGVs) and exposure assessment from all sources. EFSA Journal, 23(2): e9271.
EFSA (2026) Data collection: chemical monitoring.
European Commission (2025) Summary Report, Standing Committee on Plants, Animals, Food and Feed Section Phytopharmaceuticals – Pesticide Residues, 24–25 November 2025.
Sources
Draft Commission Regulation as regards maximum residue levels for copper compounds in or on certain products
Draft Annex II (PLAN/2025/350 draft v3)
Tables & Figures
Source: based on PLAN/2025/350 draft v3
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
EU to raise MRLs for copper compounds on certain foods
Draft Commission Regulation as regards maximum residue levels for copper compounds in or on certain products
Draft Annex II (PLAN/2025/350 draft v3)
What is changing and why?
The European Union (EU) will amend the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for copper compounds on certain products, as summarised in Table 1. This is based on updated scientific assessments by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), which reviewed all sources of exposure including use as a pesticide, as well as natural presence in the environment.
Actions
For other products not listed in Table 1, EFSA will be evaluating the possibility of lowering MRLs taking into account the natural presence of copper in those foods. There is an opportunity to submit data to EFSA in support of this evaluation until 2028 (see Full report for details).
Timeline
The Regulation is expected to be published and to apply from April 2026.
Tables & Figures

Source: based on PLAN/2025/350 draft v3
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
