Maximum residue levels for cyantraniliprole
- Pesticide MRLs
Summary
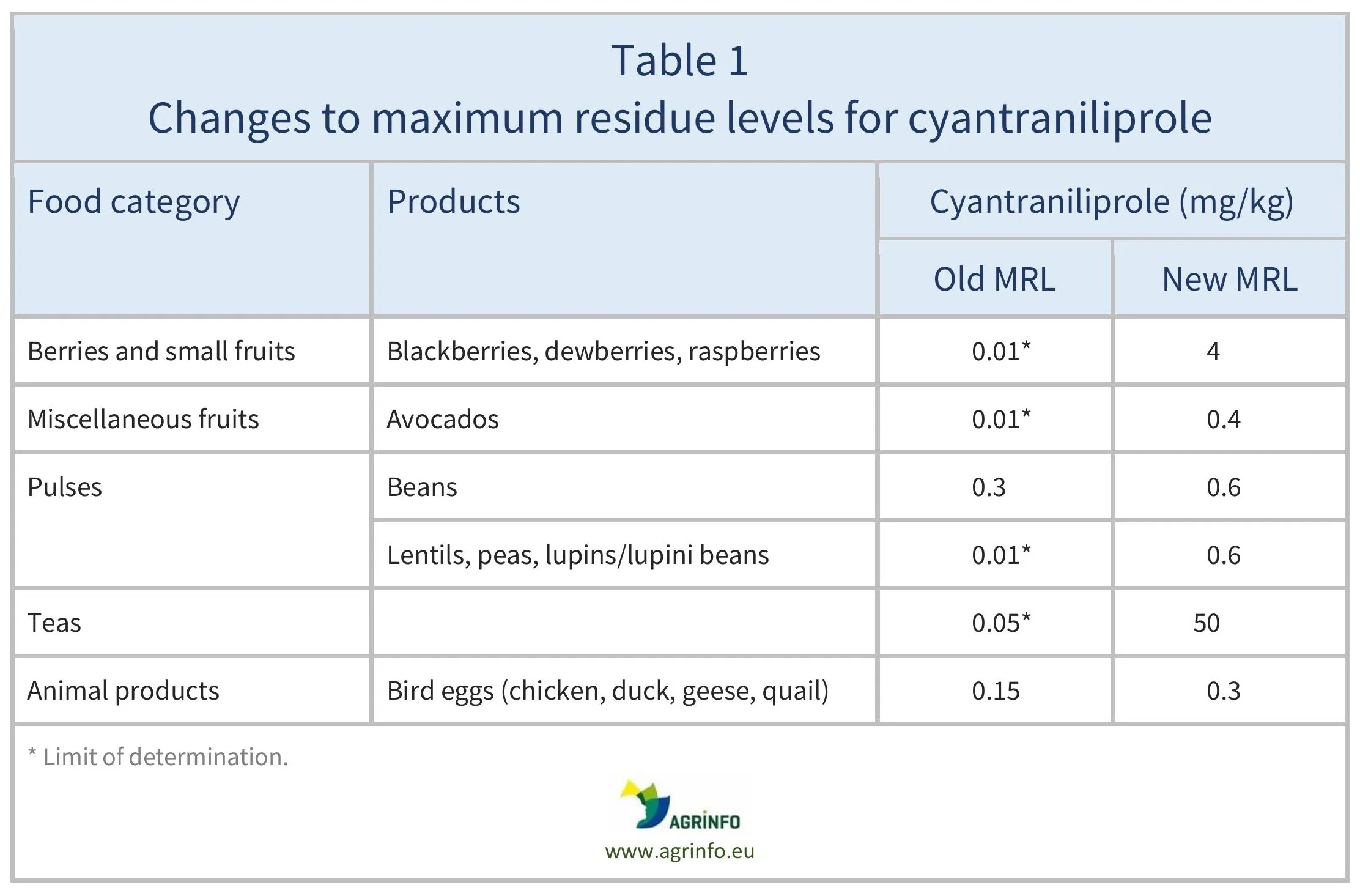
The European Union (EU) has raised the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for cyantraniliprole on blackberries, dewberries, raspberries, avocados, pulses (beans, lentils, peas, lupins), teas, and bird eggs, in line with Codex Alimentarius MRLs (CXLs) adopted in 2024.
EU raises cyantraniliprole MRLs on certain products in line with Codex standards
Commission Regulation (EU) 2025/1164 of 13 June 2025 amending Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards maximum residue levels for cyantraniliprole, cyflumetofen, deltamethrin, mefentrifluconazole, mepiquat and oxathiapiprolin in or on certain products
Update
The European Union (EU) has raised the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for cyantraniliprole on blackberries, dewberries, raspberries, avocados, pulses (beans, lentils, peas, lupins), teas, and bird eggs, in line with Codex Alimentarius MRLs (CXLs) adopted in 2024.
Impacted Products
Avocados, beans, bird eggs, blackberries, dewberries, lentils, lupins/lupini beans, peas, raspberries, teas
What is changing?
The EU has raised the MRLs for cyantraniliprole as summarised in Table 1.
Why?
In November 2024, new CXLs were adopted for cyantraniliprole (CAC 2024a). The EU has now aligned its MRLs with these CXLs, except for dry beans and grapes, where the EU expressed reservations to the Codex Alimentarius Commission due to inconsistencies in the scientific data (CAC 2024b).
Timeline
The new MRLs for cyantraniliprole apply from 6 July 2025.
Background
MRLs are set in accordance with the rules set out in Regulation 396/2005. For information on current MRLs for other substances, please consult the EU Pesticide Residues database.
Resources
CAC (2024a) Report of the 55th Session of the Codex Committee on Pesticide Residues, Chengdu, Sichuan Province, P.R. China, 3–8 June 2024. Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme, Codex Alimentarius Commission.
CAC (2024b) Comments submitted by European Union: Codex Committee on Pesticide Residues 55th Session, Chengdu, Sichuan Province, P.R. China, 3–8 June 2024. Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme, Codex Alimentarius Commission.
EFSA (2023) Scientific support for preparing an EU position in the 54th Session of the Codex Committee on Pesticide Residues (CCPR). European Food Safety Authority.
EFSA (2024) Scientific support for preparing an EU position in the 55th Session of the Codex Committee on Pesticide Residues. European Food Safety Authority.
Sources
Commission Regulation (EU) 2025/1164 as regards maximum residue levels for cyantraniliprole, cyflumetofen, deltamethrin, mefentrifluconazole, mepiquat and oxathiapiprolin in or on certain products
Tables & Figures
Source: based on Regulation (EU) 2025/1164
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
EU raises cyantraniliprole MRLs on certain products in line with Codex standards
Commission Regulation (EU) 2025/1164 as regards maximum residue levels for cyantraniliprole, cyflumetofen, deltamethrin, mefentrifluconazole, mepiquat and oxathiapiprolin in or on certain products
What is changing and why?
The EU has raised the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for cyantraniliprole on blackberries, dewberries, raspberries, avocados, pulses (beans, lentils, peas, lupins), teas, and bird eggs, in line with Codex MRLs (CXLs) adopted in 2024. The changes are summarised in Table 1.
Timeline
The new MRLs for cyantraniliprole apply from 6 July 2025.
Tables & Figures

Source: based on Regulation (EU) 2025/1164
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
