Maximum residue levels for diazinon
- Food safety
- Pesticide MRLs
Summary
The European Union (EU) is discussing a new draft proposal to set maximum residue levels (MRLs) for diazinon on various products at the limit of determination (LOD, the lowest level that can be detected using the most modern and reliable analytical methods). This could have particular impacts on exports of almonds, cranberries, pineapples, radishes, onions, sweet peppers, sweet corn, kohlrabies, hops, seed spices, and sugar beet roots.
EU discusses reducing diazinon MRLs on various products
Draft Commission Regulation amending Annexes II, III and V to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards maximum residue levels for diazinon in or on certain products
Draft Annex II (PLAN/2025/3159)
Update
The European Union (EU) is discussing a new draft proposal to set maximum residue levels (MRLs) for diazinon on various products at the limit of determination (LOD, the lowest level that can be detected using the most modern and reliable analytical methods). This could have particular impacts on exports of almonds, cranberries, pineapples, radishes, onions, sweet peppers, sweet corn, kohlrabies, hops, seed spices, and sugar beet roots.
Impacted Products
Almonds, Brazil nuts, cashew nuts, chestnuts, coconuts, hazelnuts/cobnuts, macadamias, pecans, pine nut kernels, pistachios, walnuts, cranberries, pineapples, radishes, garlic, onions, shallots, spring onions/green onions, Welsh onions, sweet peppers/bell peppers, sweet corn, Chinese cabbages/pe-tsai, kohlrabies, linseeds, peanuts/groundnuts, poppy seeds, sesame seeds, sunflower seeds, rapeseed/canola seeds, soyabeans, mustard seeds, cotton seeds, pumpkin seeds, safflower seeds, borage seed, gold of pleasure seeds, hemp seeds, castor beans, olives for oil production, oil palm kernels, oil palm fruits, kapok, hops, anise/aniseed, black caraway/black cumin, celery, coriander, cumin, dill, fennel, fenugreek, nutmeg, allspice/pimento, Sichuan pepper, caraway, cardamom, juniper berry, peppercorn (black, green, white), vanilla, tamarind, liquorice, turmeric/curcuma, sugar beet roots, muscle (swine, cattle, sheep, goat, poultry), fat (swine, cattle, sheep, goat), liver, kidney (swine, cattle, sheep, goat), edible offals (poultry), milk (cattle, sheep, goat, horse), bird eggs (chicken, duck, geese, quail), honey and other apiculture products
What is changing?
The European Commission initially proposed to reduce the MRLs for diazinon on certain products to the LOD of 0.01 mg/kg. It has now drafted a new proposal that considers maintaining the MRLs for certain animal products due to the presence of diazinon in authorised veterinary medicinal products.
The proposed changes are summarised in Table 1.
Why?
The MRLs for diazinon that have been in place since the adoption of Regulation 396/2005 have never been reviewed. Following a series of evaluations and a stakeholder consultation (see EFSA invites submission of data to support review of certain MRLs), the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has concluded that the existing MRLs are not substantiated (EFSA 2023). This new proposal also takes into account the presence of this substance in veterinary medicinal products.
Timeline
The Regulation is expected to be published in 2026 and will apply 6 months after publication.
Recommended Actions
Suppliers of almonds, cranberries, pineapples, radishes, onions, sweet peppers, sweet corn, kohlrabies, hops, seed spices, and sugar beet roots should explore chemical and non-chemical solutions as an alternative to the use of diazinon.
Background
MRLs are set in accordance with the rules set out in Regulation 396/2005. For information on current MRLs for other substances, please consult the EU Pesticide Residues database.
For further information on the EU’s process and principles for setting MRLs, see Regulation of pesticide residues in the EU – Questions and Answers.
Resources
EFSA (2023) Targeted review of maximum residue levels (MRLs) for diazinon. EFSA Journal, 21(11): e08426.
European Commission (2025) Standing Committee on Plants, Animals, Food and Feed, Section Phytopharmaceuticals – Residues, 24–25 November 2025.
Draft Commission Regulation amending Annexes II, III and V to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards maximum residue levels for azocyclotin, chlorfenapyr, cyhexatin, diazinon, dicofol, endosulfan, fenarimol, fenpropathrin and profenofos in or on certain products
Sources
Draft Commission Regulation as regards maximum residue levels for diazinon in or on certain products
Draft Annex II (PLAN/2025/3159)
Tables & Figures
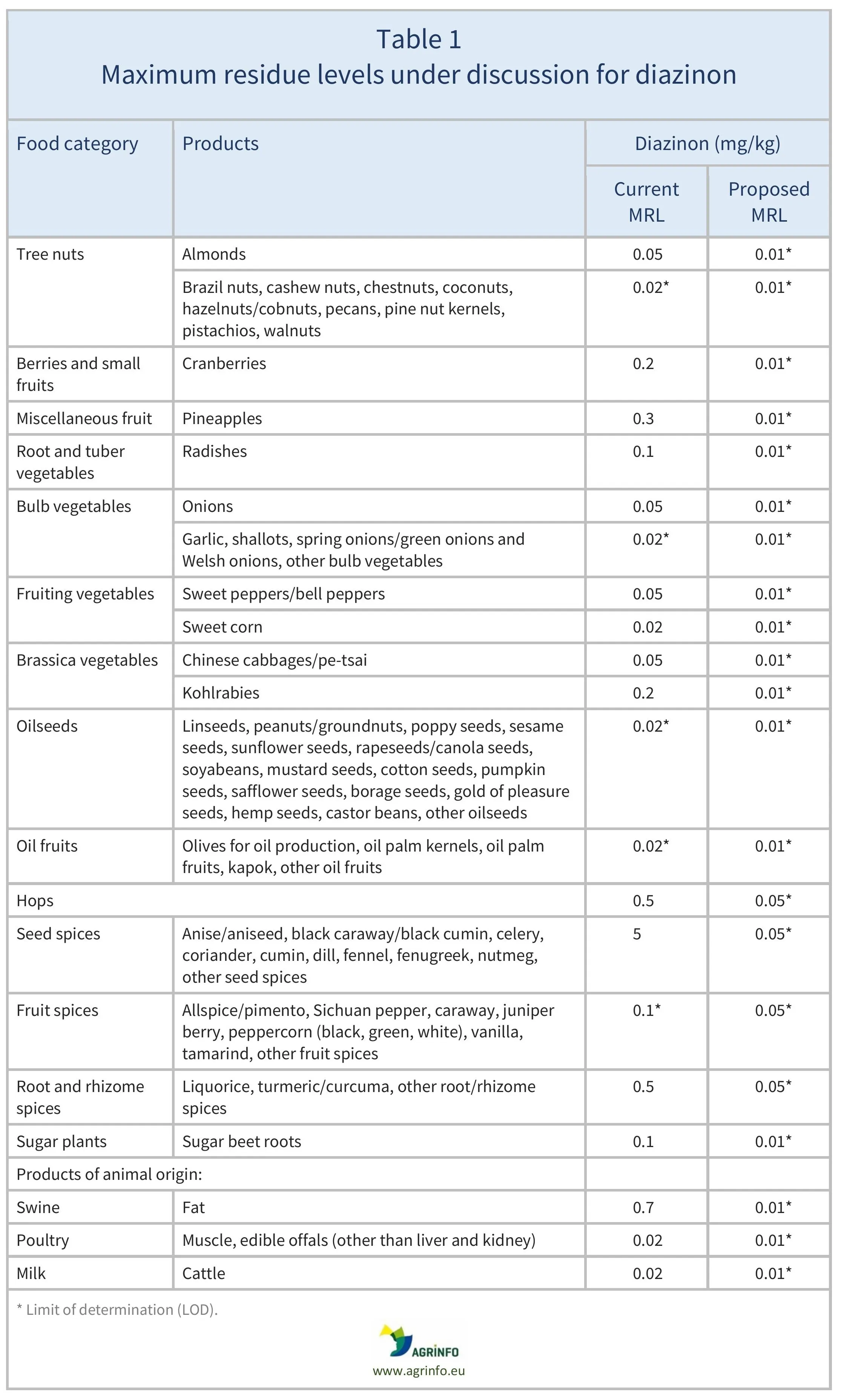
Source: based on PLAN/2025/3159_Annex II_v0
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
EU discusses reducing diazinon MRLs on various products
Draft Commission Regulation as regards maximum residue levels for diazinon in or on certain products
Draft Annex II (PLAN/2025/3159)
What is changing and why?
The European Union (EU) is discussing revising the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for diazinon. The European Commission initially proposed to reduce the MRLs for diazinon on certain products to the LOD of 0.01 mg/kg; this could have particular impacts on exports of almonds, cranberries, pineapples, radishes, onions, sweet peppers, sweet corn, kohlrabies, hops, seed spices, and sugar beet roots. It has now drafted a new proposal that considers maintaining the MRLs for certain animal products due to the presence of diazinon in authorised veterinary medicinal products.
Actions
Suppliers of almonds, cranberries, pineapples, radishes, onions, sweet peppers, sweet corn, kohlrabies, hops, seed spices, and sugar beet roots should explore chemical and non-chemical solutions as an alternative to the use of diazinon.
Timeline
The Regulation is expected to be published in 2026 and will apply 6 months after publication.
Tables & Figures

Source: based on PLAN/2025/3159_Annex II_v0
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
