Maximum residue levels for ethephon
- Food safety
- Pesticide MRLs
Summary
The European Union (EU) has amended the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for ethephon.
Revised MRLs will have a particular impact on exporters of blueberries and tree nuts (except hazelnuts and walnuts) where the MRL will be reduced to the limit of determination (LOD). (The LOD is the lowest level that can be detected using the most modern and reliable analytical methods.)
MRLs are also reduced on apples, pineapples, rye, and wheat. The MRL for barley is increased. The EU has also lowered the LODs on a wide range of products.
EU amends MRLs for ethephon
Commission Regulation (EU) 2026/215 of 29 January 2026 amending Annexes II and V to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards maximum residue levels for dimoxystrobin, ethephon and propamocarb in or on certain products
Update
The European Union (EU) has amended the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for ethephon.
Revised MRLs will have a particular impact on exporters of blueberries and tree nuts (except hazelnuts and walnuts) where the MRL will be reduced to the limit of determination (LOD). (The LOD is the lowest level that can be detected using the most modern and reliable analytical methods.)
MRLs are also reduced on apples, pineapples, rye, and wheat. The MRL for barley is increased. The EU has also lowered the LODs on a wide range of products.
Impacted Products
Grapefruits, oranges, lemons, limes, mandarins, almonds, Brazil nuts, cashew nuts, chestnuts, coconuts, macadamias, pecans, pine nut kernels, pistachios, apples, quinces, medlars, loquats/Japanese medlars, apricots, peaches, blackberries, dewberries, raspberries, blueberries, cranberries, currants, gooseberries, rose hips, mulberries, elderberries, dates, kumquats, carambolas, jambolans, kiwi fruits, lychees, passionfruits, prickly pears, star apples, American persimmons/Virginia kaki, avocados, bananas, mangoes, papayas, granate apples/pomegranates, cherimoyas, guavas, pineapples, breadfruits, durians, soursops/guanabanas, potatoes, cassava roots/manioc, sweet potatoes, yams, arrowroots, beetroots, carrots, celeriacs, horseradishes, Jerusalem artichokes, parsnips, parsley roots, parsley, radishes, salsifies, swedes/rutabagas, turnips, garlic, onions, shallots, spring onions/green onions and Welsh onions, sweet peppers/bell peppers, aubergines/eggplants, okra/lady’s fingers, cucumbers, gherkins, courgettes, melons, pumpkins, watermelons, sweet corn, broccoli, cauliflowers, Brussels sprouts, head cabbages, Chinese cabbages/pe-tsai, kales, kohlrabies, lamb’s lettuces/corn salads, lettuces, escaroles/broad-leaved endives, cresses and other sprouts and shoots, land cresses, Roman rocket/rucola, red mustards, baby leaf crops (including Brassica species), spinaches, purslanes, chards/beet leaves, grape leaves, watercresses, witloofs/Belgian endives, chervil, chives, celery leaves, parsley, sage, rosemary, thyme, basil and edible flowers, laurel/bay leaves, tarragon, beans (with pods), beans (without pods), peas (with pods), peas (without pods), lentils, asparagus, cardoons, celeries, Florence fennels, globe artichokes, leeks, rhubarbs, bamboo shoots, palm hearts, cultivated fungi, wild fungi, mosses and lichens, algae and prokaryotes, beans (dry), lentils (dry), peas (dry), lupins/lupini beans, linseeds, peanuts/groundnuts, poppy seeds, sesame seeds, sunflower seeds, rapeseeds/canola seeds, soyabeans, mustard seeds, pumpkin seeds, safflower seeds, borage seeds, gold of pleasure seeds, hemp seeds, castor beans, oil palm kernels, oil palm fruits, kapok, barley, buckwheat, pseudocereals, maize/corn, common millet/proso millet, oats, rice, rye, sorghum, wheat, teas, coffee beans, chamomile, hibiscus/roselle, rose, jasmine, lime/linden, strawberry, rooibos, maté, valerian, ginseng, cocoa beans, carobs/Saint John’s breads, hops, anise/aniseed, black caraway/black cumin, celery, coriander, cumin, dill, fennel, fenugreek, nutmeg, fruit spices, allspice/pimento, Sichuan pepper, caraway, cardamom, juniper berry, peppercorn (black, green, white), vanilla, tamarind, cinnamon, liquorice, turmeric/curcuma, cloves, capers, saffron, mace, sugar beet roots, sugar canes, chicory roots, milk (cattle, sheep, goat, horse), birds’ eggs (chicken, duck, geese, quail), amphibians, reptiles, terrestrial invertebrate animals, wild terrestrial vertebrate animals
What is changing?
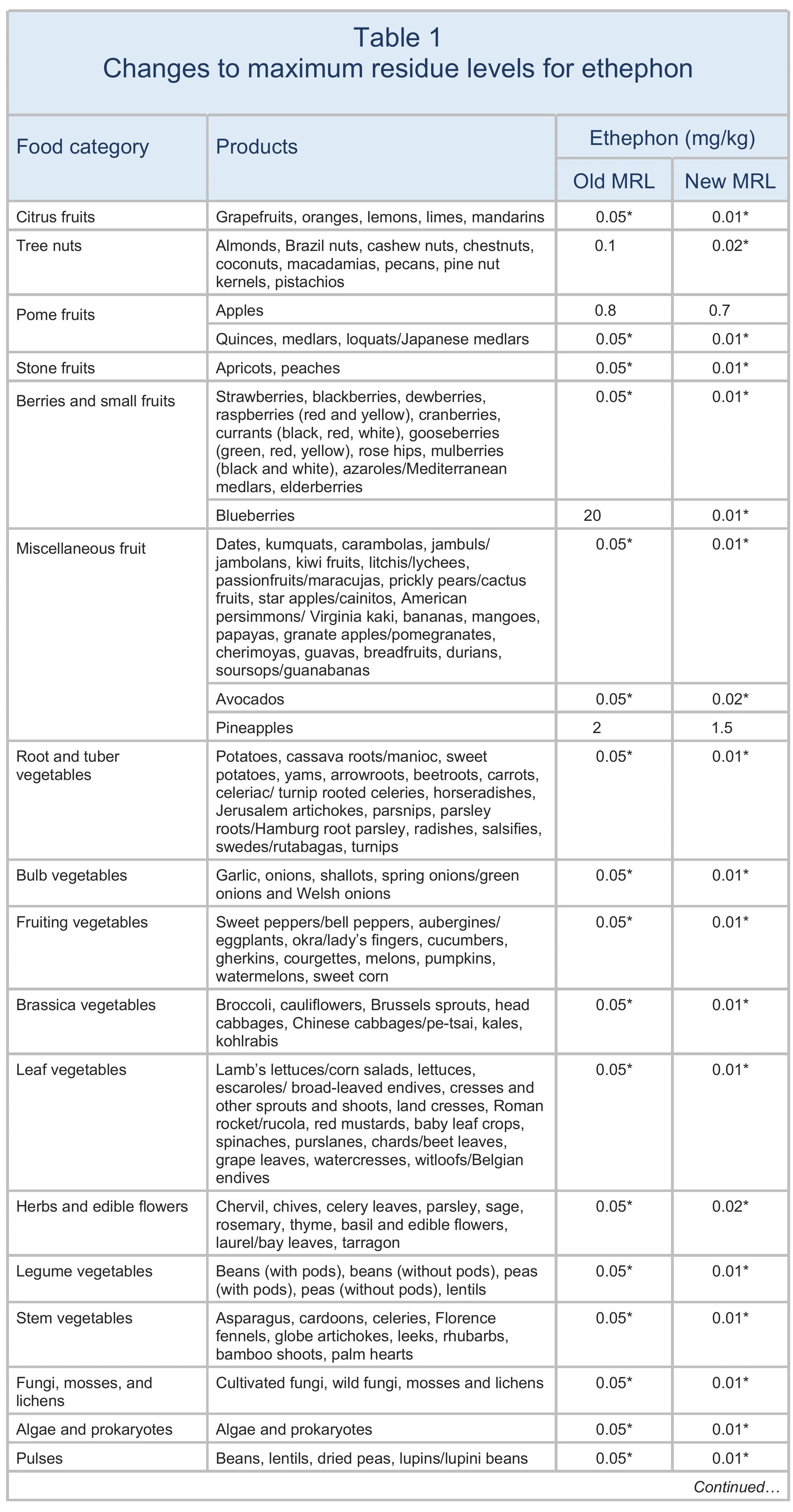
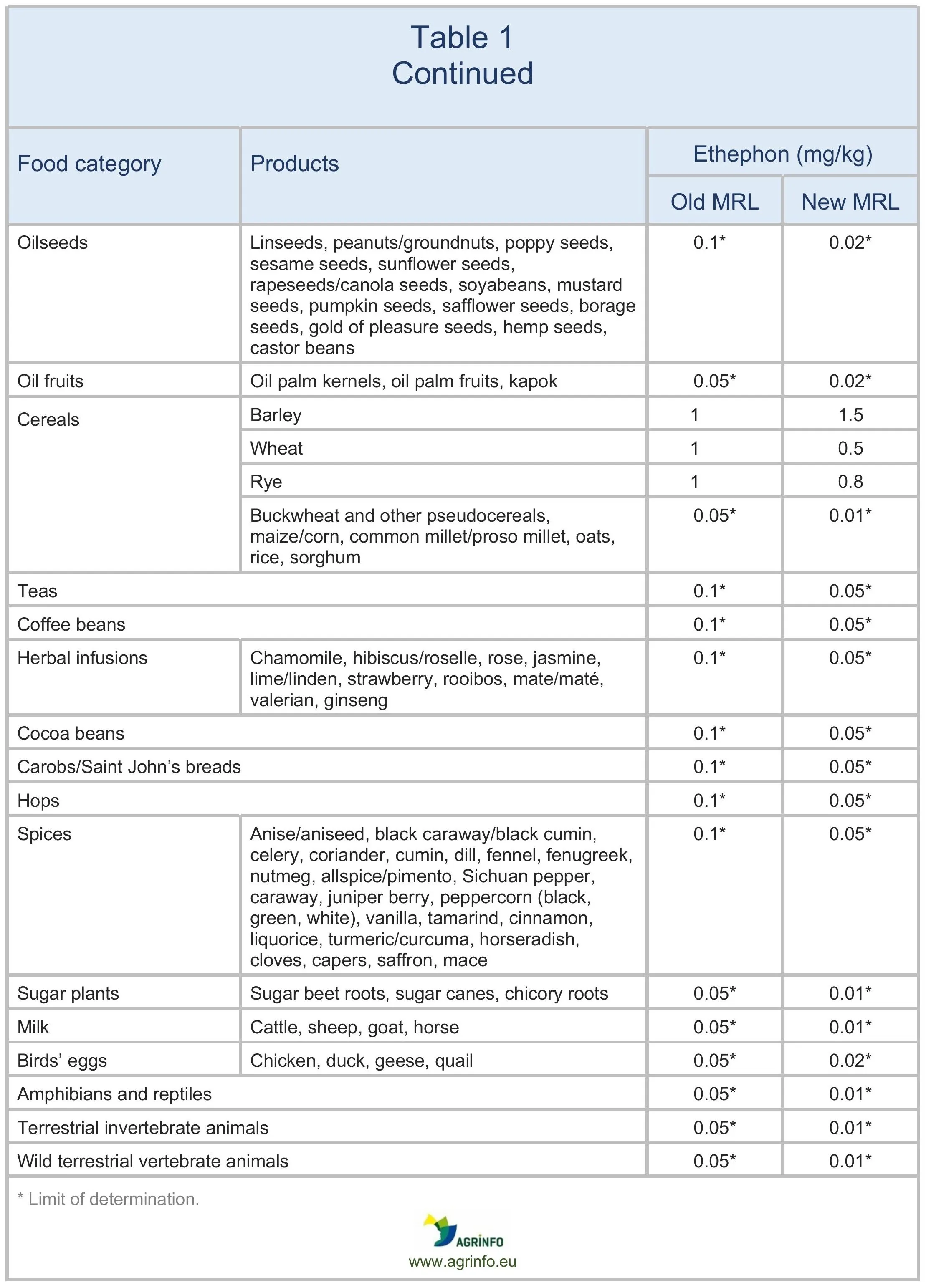
The EU has amended the MRLs for ethephon as summarised in Table 1.
Why?
When the EU renewed its approval for ethephon (see EU pesticide approvals, renewals, and extensions in 2023), the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) recommended lowering the acceptable daily intake (ADI) for this substance (EFSA 2023). Based on this reduced ADI, EFSA (2024) reviewed all MRLs for ethephon.
The European Commission also consulted the EU Reference Laboratories for residues of pesticides as regards the need to adapt certain LODs. Those laboratories proposed product-specific LODs for ethephon that are analytically achievable, ensuring compliance with updated safety and monitoring standards.
Timeline
The new MRLs apply from 19 August 2026.
Recommended Actions
Suppliers of apples, pineapples, rye, and wheat should review their current use of ethephon and assess whether any changes will be needed to existing good agricultural practices (GAPs) to ensure compliance with the new MRLs. Suppliers of blueberries and affected nuts should evaluate their current use of ethephon and explore possible alternative solutions.
Background
MRLs are set in accordance with the rules set out in Regulation 396/2005. For information on current MRLs for other substances, please consult the EU Pesticide Residues database.
Resources
EFSA (2023) Peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance ethephon. EFSA Journal, 21(1): 7742.
EFSA (2024) Targeted review of the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for ethephon. EFSA Journal, 22(4): e8757.
Sources
Commission Regulation (EU) 2026/215 as regards maximum residue levels for dimoxystrobin, ethephon and propamocarb in or on certain products
Tables & Figures
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
EU amends MRLs for ethephon
Commission Regulation (EU) 2026/215 as regards maximum residue levels for dimoxystrobin, ethephon and propamocarb in or on certain products
What is changing and why?
When the European Union (EU) renewed its approval for ethephon, the European Food Safety Authority recommended lowering the acceptable daily intake (ADI) for this substance. The EU has amended the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for ethephon as summarised in Table 1.
Revised MRLs will have a particular impact on exporters of blueberries and tree nuts (except hazelnuts and walnuts), for which the MRL will be reduced to the limit of determination (LOD). (The LOD is the lowest level that can be detected using the most modern and reliable analytical methods.)
Actions
Suppliers of apples, pineapples, rye, and wheat should review their current use of ethephon and assess whether any changes will be needed to existing good agricultural practices (GAPs) to ensure compliance with the new MRLs. Suppliers of blueberries and affected nuts in particular should evaluate their current use of ethephon and explore possible alternative solutions in anticipation of these MRL changes.
Timeline
The new MRLs apply from 19 August 2026.
Tables & Figures
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.