Maximum residue levels for oxamyl
- Pesticide MRLs
- Pesticides
Summary
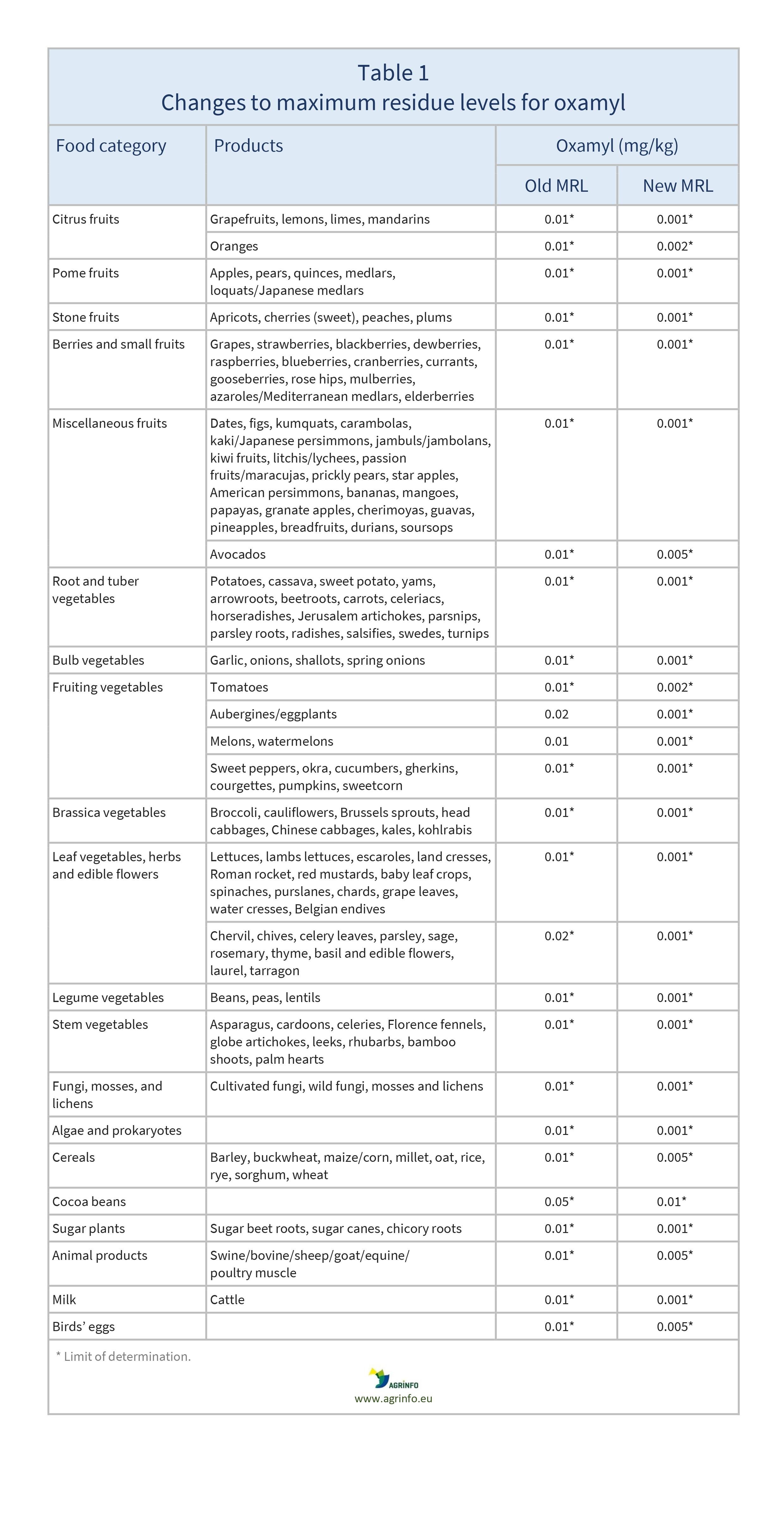
The EU has lowered the maximum residue limits (MRLs) for oxamyl, with particular impacts on eggplants, melons, and watermelons. For all products, the limit of determination (LOD, the lowest level that can be detected using the most modern and reliable analytical methods) is also being reduced. The changes will apply from 11 May 2024.
EU lowers MRLs for oxamyl on all products
Commission Regulation 2024/331 amending Annexes II and V to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards maximum residue levels for oxamyl in or on certain products
Update
The EU has lowered the maximum residue limits (MRLs) for oxamyl, with particular impacts on eggplants, melons, and watermelons. For all products, the limit of determination (LOD, the lowest level that can be detected using the most modern and reliable analytical methods) is also being reduced. The changes will apply from 11 May 2024.
Impacted Products
All products, particularly aubergines/eggplants, melons, and watermelons.
Citrus fruits, grapefruits, lemons, limes, mandarins, oranges, pome fruits, apples, pears, quinces, medlars, loquats/ Japanese medlars, stone fruits, apricots, cherries (sweet), peaches, plums, berries and small fruits, grapes, strawberries, blackberries, dewberries, raspberries, blueberries, cranberries, currants, gooseberries, rose hips, mulberries, azaroles/ Mediterranean medlars, elderberries, miscellaneous fruits, dates, figs, kumquats, carambolas, kaki/ Japanese persimmons, jambuls/ jambolans, kiwi fruits, litchis/ lychees, passion fruits/ maracujas, prickly pears, star apples, American persimmons, bananas, mangoes, papayas, granate apples, cherimoyas, guavas, pineapples, breadfruits, durians, soursops, avocados, root and tuber vegetables, potatoes, cassava, sweet potato, yams, arrowroots, beetroots, carrots, celeriacs, horseradishes, Jerusalem artichokes, parsnips, parsley roots, radishes, salsifies, swedes, turnips, bulb vegetables, garlic, onions, shallots, spring onions, fruiting vegetables, tomatoes, aubergines/ eggplants, melons, watermelons, sweet peppers, okra, cucumbers, gherkins, courgettes, pumpkins, sweetcorn, brassica vegetables, broccoli, cauliflowers, brussels sprouts, head cabbages, Chinese cabbages, kales, kohlrabis, leaf vegetables, herbs and edible flowers, lettuces, lambs lettuces, escaroles, land cresses, Roman rocket, red mustards, baby leaf crops, spinaches, purslanes, chards, grape leaves, water cresses, Belgian endives, chervil, chives, celery leaves, parsley, sage, rosemary, thyme, basil and edible flowers, laurel, tarragon, legume vegetables, beans, peas, lentils, stem vegetables, asparagus, cardoons, celeries, Florence fennels, globe artichokes, leeks, rhubarbs, bamboo shoots, palm hearts, fungi, mosses, and lichens, cultivated fungi, wild fungi, mosses and lichens, algae and prokaryotes, cereals, barley, buckwheat, maize/ corn, millet, oat, rice, rye, sorghum, wheat, cocoa beans, sugar plants, sugar beet roots, sugar canes, chicory roots, animal products, swine/ bovine/ sheep/ goat/ equine/ poultry muscle, milk, cattle, birds’ eggs
What is changing?
The EU has reduced the LOD for all products listed in Table 1. Most of these values are lower than the standard default LOD of 0.01 mg/kg.
Why?
All MRLs for oxamyl were already set at the LOD, except for aubergines, melons, and watermelons. However, EFSA (2022) concluded that the default LOD of 0.01 mg/kg does not provide sufficient protection for consumers for most commodities, so the LOD for these products should be set at lower, more protective levels (0.005, 0.002, or 0.001 mg/kg). MRLs for aubergine, melon, and watermelon (which were based on Codex MRLs) are also considered not to provide a sufficient level of protection, and are reduced to the LOD.
Timeline
The new MRLs will apply from 11 May 2024. All products on the EU market after 11 May 2024 must comply with the new MRLs, even if they were put on the market before that date. Products exported before 11 May 2024 should therefore also be checked for their compliance with the new MRLs.
Recommended Actions
Exporters of aubergines, melons, and watermelons should urgently review their current use of oxamyl and look for alternative solutions in anticipation of the MRL changes.
Pesticide residue monitoring needs to take into account the new lower LODs set out in Table 1. This change has implications for laboratories conducting pesticide residue analyses, depending on the methods used. Non-EU authorities can seek advice from EU Reference Laboratories (EURL) on how to achieve these lower levels in residue analysis: contact the EURL for Single Residue Methods (EURL-SRM) concerning pesticides not amenable to multiresidue methods in all types of matrices by emailing EURL-SRM@cvuas.bwl.de.
Background
MRLs are set in accordance with the rules set out in Regulation 396/2005. For information on current MRLs for other substances, please consult the EU Pesticide Residues database.
Resources
EFSA (2022) Peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance oxamyl. EFSA Journal, 20(5): 7296.
Sources
Commission Regulation (EU) 2024/331 as regards maximum residue levels for oxamyl in or on certain products
Tables & Figures
Source: based on Commission Regulation 2024/331
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
EU lowers MRLs for oxamyl on all products
Commission Regulation 2024/331 as regards maximum residue levels for oxamyl in or on certain products
What is changing and why?
The EU has lowered the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for oxamyl to the limit of determination (LOD, the lowest level that can be detected using the most modern and reliable analytical methods).
The LOD for these and all other products is also reduced to below the standard default LOD of 0.01 mg/kg to protect consumers (see Table 1).
This may particularly have impacts on exporters of aubergines/ eggplants (current MRL 0.02 mg/kg), and melons and watermelons (current MRL 0.01 mg/kg).
Actions
Exporters of aubergines, melons, and watermelons should urgently review their current use of oxamyl and look for alternative solutions in anticipation of the MRL changes. Exporters of all the products listed in Table 1 should review their monitoring/ analysis of pesticide residues to take into account MRLs set below 0.01 mg/kg.
Pesticide residue monitoring needs to take into account the new lower LODs set out in Table 1. Testing for levels below 0.01 mg/kg will affect how laboratories carry out pesticide residue analysis. Non-EU authorities can seek advice from EU Reference Laboratories (EURL) on how to achieve these lower levels in residue analysis: contact the EURL for Single Residue Methods (EURL-SRM) by emailing EURL-SRM@cvuas.bwl.de.
Timeline
The new MRLs apply from 11 May 2024. All products on the EU market after 11 May 2024 must comply with the new MRLs, even if they were put on the market before that date. Products exported before May 2024 should therefore also be checked for their compliance with the new MRLs.
Tables & Figures

Source: based on Commission Regulation 2024/331
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
