Reports on non-compliance with EU food law and agri-food fraud: July 2024
- Contaminants
- Food safety
- Food supplements/dietetic foods
- Pesticide MRLs
- Pesticides
- Veterinary residues
- Food safety controls
- Official controls
Summary
The European Commission publishes monthly overviews of foods that are not compliant with EU food law. The July 2024 report includes notifications concerning the following 38 AGRINFO partner countries: Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Argentina, Bolivia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Brazil, Cambodia, China, Colombia, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Egypt, Guinea, India, Iran, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kenya, Lebanon, Mauritania, Mexico, Moldova, Pakistan, Paraguay, Peru, Philippines, Republic of North Macedonia, Rwanda, Serbia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Syria, Thailand, Tunisia, Türkiye, Ukraine, Vietnam.
These monthly overviews highlight ongoing and emerging risks of non-compliance that will help agri-food exporters and competent authorities in non-EU countries to monitor and respond to risks that may affect trade.
Latest EU overview of food found not to comply with EU law
European Commission: July 2024 report on EU agri-food fraud suspicions
Update
The European Commission publishes monthly overviews of foods that are not compliant with EU food law. The July 2024 report includes notifications concerning the following 38 AGRINFO partner countries: Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Argentina, Bolivia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Brazil, Cambodia, China, Colombia, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Egypt, Guinea, India, Iran, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kenya, Lebanon, Mauritania, Mexico, Moldova, Pakistan, Paraguay, Peru, Philippines, Republic of North Macedonia, Rwanda, Serbia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Syria, Thailand, Tunisia, Türkiye, Ukraine, Vietnam.
These monthly overviews highlight ongoing and emerging risks of non-compliance that will help agri-food exporters and competent authorities in non-EU countries to monitor and respond to risks that may affect trade.
Impacted Products
Cephalopods and their products; cereals and bakery products; cocoa, coffee and tea; confectionery; crustaceans and their products; dietetic foods; fats and oils; fish and fish products; food contact materials; food supplements and fortified foods; fruits and vegetables; herbs and spices; honey and royal jelly; ices and deserts; meat and its products; milk and milk products; non-alcoholic beverages; nuts, nut products and seeds; poultry meat and its products; prepared dishes and snacks; soups, broths, sauces, and condiments
Notifications
The July 2024 report includes notifications impacting the following 38 AGRINFO partner countries:
Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Argentina, Bolivia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Brazil, Cambodia, China, Colombia, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Egypt, Guinea, India, Iran, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kenya, Lebanon, Mauritania, Mexico, Moldova, Pakistan, Paraguay, Peru, Philippines, Republic of North Macedonia, Rwanda, Serbia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Syria, Thailand, Tunisia, Türkiye, Ukraine, Vietnam.
These notifications concern:
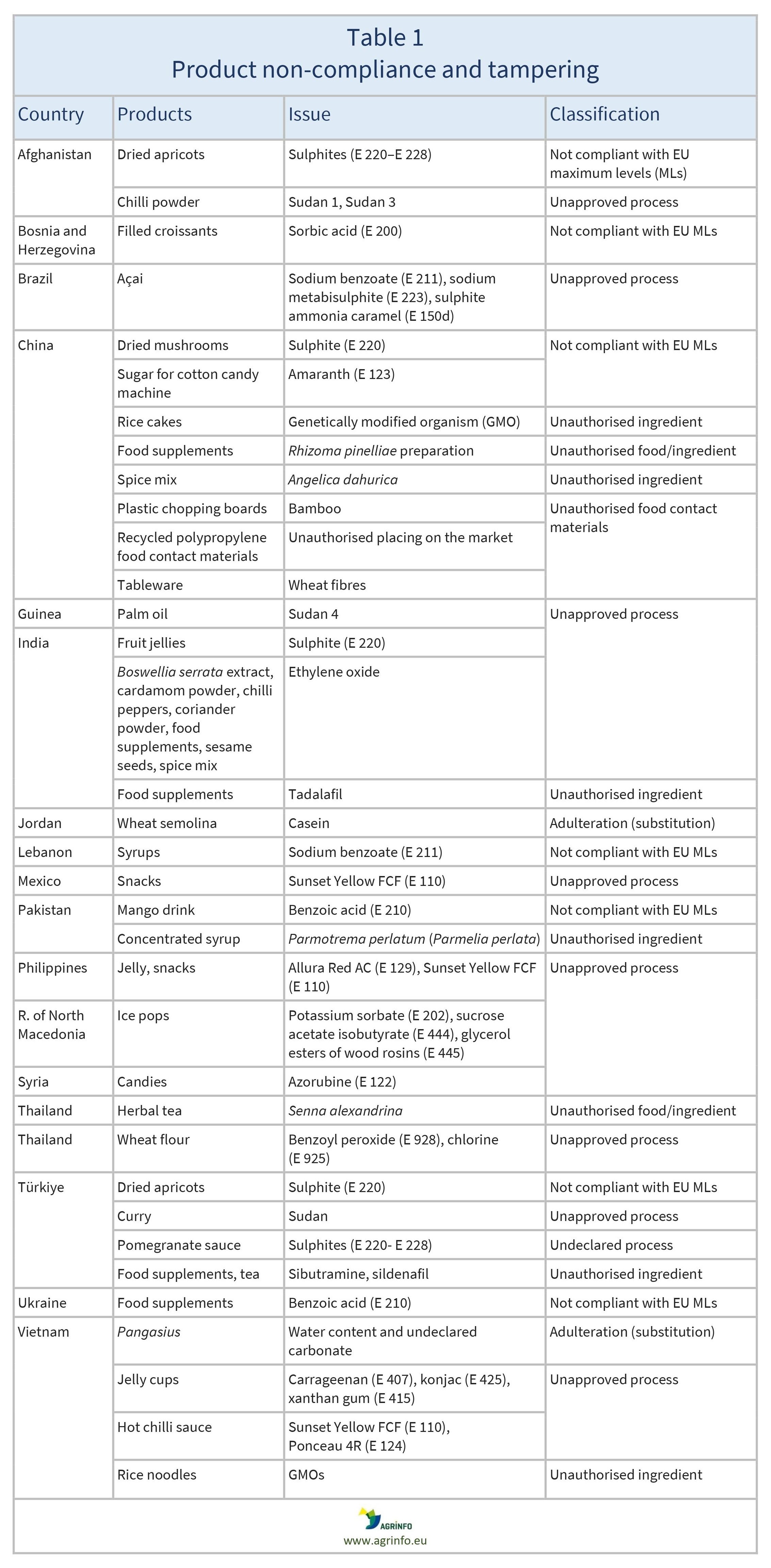
- product non-compliance and tampering (Table 1)
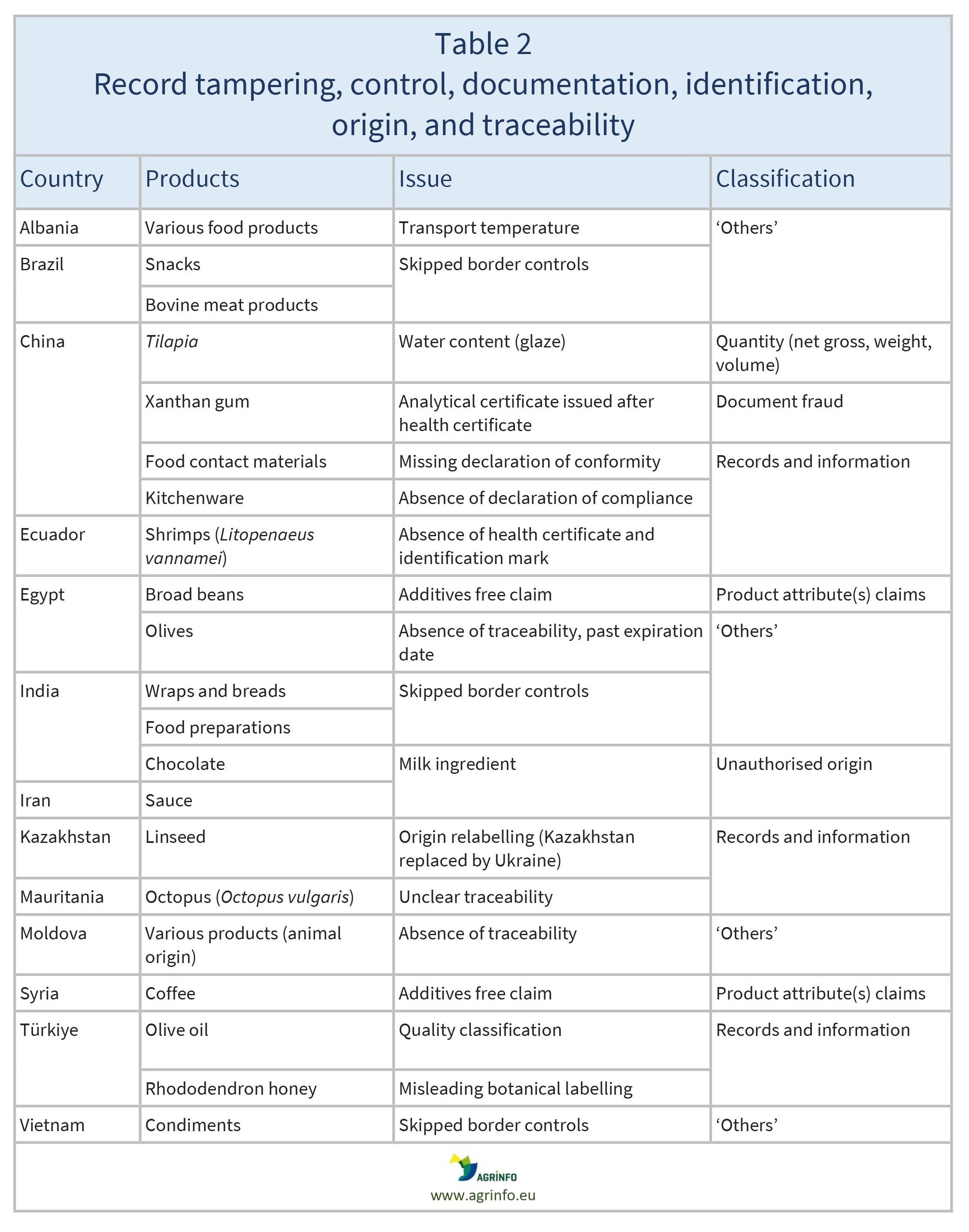
- record tampering, avoidance of control, false or deficient documentation (including mislabelling), identification, origin, and traceability defects (Table 2)
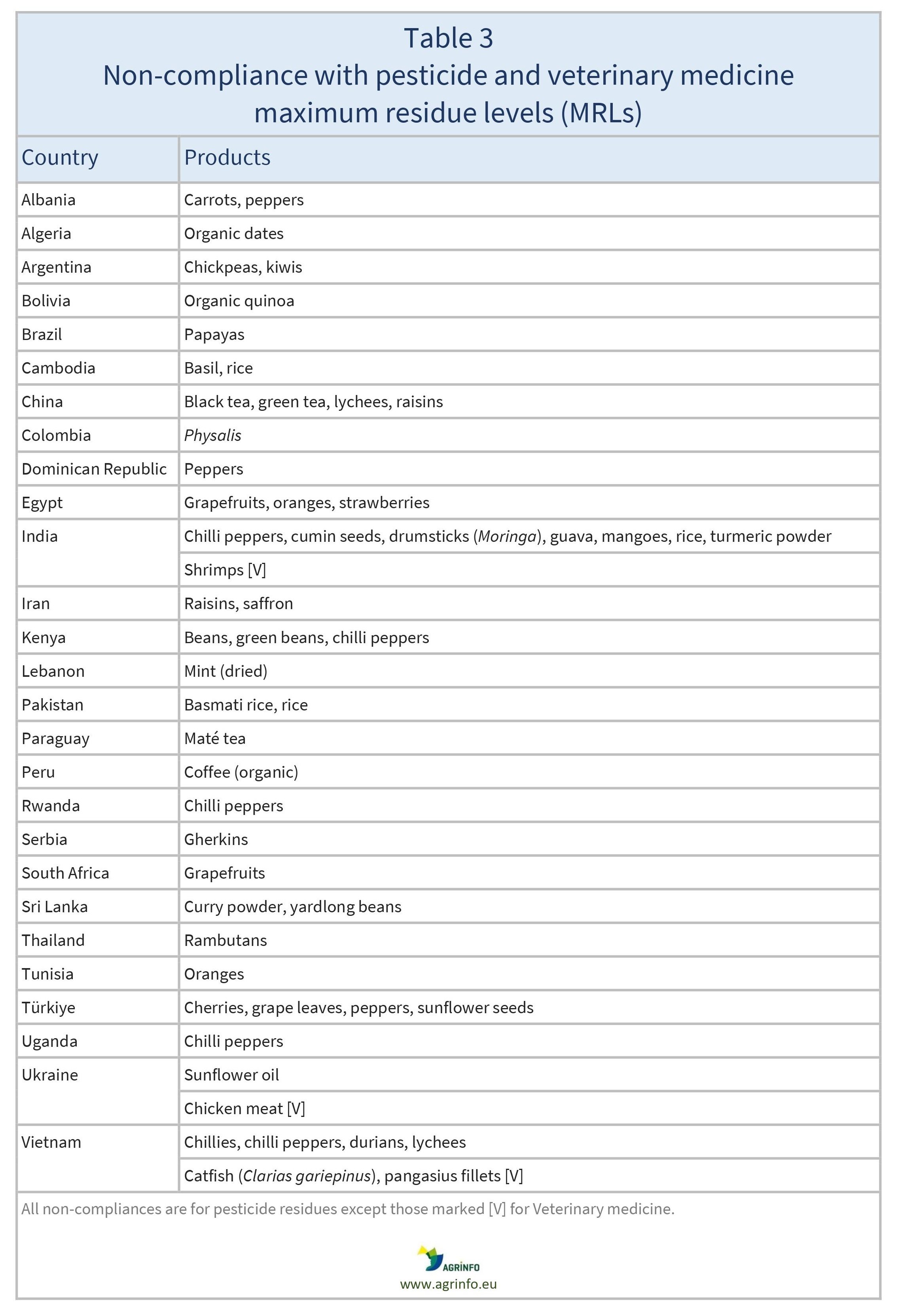
- non-compliance with maximum residue levels (MRLs) for pesticides and veterinary medicines (Table 3).
See RASFF notifications in July 2024.
Timeline
These reports are issued every month.
Recommended Actions
Competent authorities in countries that are included in these monthly overviews should pay attention to any non-compliances identified in the reports. It is particularly important that the producer-export companies concerned are informed as soon as possible so that they can take action and prevent a recurrence. These incidents also potentially indicate a more widespread problem that may require a coordinated response by the food sector in the country concerned.
Background
These monthly reports compile information notified to the EU’s Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed Network (RASFF), Administrative Assistance and Cooperation Network (AAC), and Agri-Food Fraud Network (FFN). The reports also include non-compliances with EU rules that do not present a risk, but have triggered investigations by the competent authorities of individual importing EU Member States.
Resources
Monthly reports on EU agri-food fraud suspicions
Regulation 2019/1793 on the temporary increase of official controls and emergency measures governing entry into the EU of certain goods from third countries
Regulation 2019/1873 on the procedures at border control posts for a coordinated performance by competent authorities of intensified official controls on products of animal origin, germinal products, animal by-products and composite products
Sources
European Commission: July 2024 report on EU agri-food fraud suspicions
Tables & Figures
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
Latest EU overview of food found not to comply with EU law
European Commission: July 2024 report on EU agri-food fraud suspicions
What is changing and why?
The European Commission publishes monthly overviews of foods that are not compliant with EU food law, including potentially fraudulent practices identified and reported by EU Member State authorities, based on Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed Network (RASFF) notifications among other sources. These reports help stakeholders in the agri-food sector to identify risks and adapt monitoring strategies.
The July 2024 report includes notifications impacting 38 AGRINFO partner countries: Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Argentina, Bolivia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Brazil, Cambodia, China, Colombia, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Egypt, Guinea, India, Iran, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kenya, Lebanon, Mauritania, Mexico, Moldova, Pakistan, Paraguay, Peru, Philippines, Republic of North Macedonia, Rwanda, Serbia, South Africa, Sri Lanka, Syria, Thailand, Tunisia, Türkiye, Ukraine, Vietnam.
See Tables 1–3 for details.
Actions
Competent authorities in countries that are included in these monthly overviews should pay attention to any non-compliances identified in the reports. It is particularly important that the producers/export companies concerned are informed as soon as possible so that they can take action and prevent a recurrence. These incidents also potentially indicate a more widespread problem that may require a coordinated response by the food sector in the country concerned.
Timeline
A report is issued every month.
Tables & Figures



Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
