Revision of permitted substances for use in organic production (2025)
- Organic production
Summary
The EU has authorised the use of protein from peas and potatoes for the clarification of fruit juices, fruit wines, and mead. These will be included in the list of substances that may be used to produce organic products for the European Union (EU) market.
The European Commission’s Expert Group for Technical Advice on Organic Production (EGTOP) has started an evaluation of substances to be authorised for cleaning and disinfection in organic production. As this evaluation is taking longer than anticipated, the list of substances currently authorised for cleaning and disinfection of buildings and installations for animal production will continue to apply until 31 December 2027.
EU authorises pea/potato protein and delays review of disinfectants
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2025/2501 of 11 December 2025 amending Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/1165 as regards the use of certain products and substances in organic production
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2025/973 of 23 May 2025 amending and correcting Implementing Regulation (EU) 2021/1165 authorising certain products and substances for use in organic production and establishing their lists
Update
The EU has authorised the use of protein from peas and potatoes for the clarification of fruit juices, fruit wines, and mead. These will be included in the list of substances that may be used to produce organic products for the European Union (EU) market.
The European Commission’s Expert Group for Technical Advice on Organic Production (EGTOP) has started an evaluation of substances to be authorised for cleaning and disinfection in organic production. As this evaluation is taking longer than anticipated, the list of substances currently authorised for cleaning and disinfection of buildings and installations for animal production will continue to apply until 31 December 2027.
Impacted Products
Organic fruit juices, fruit wines, mead
What is changing?
Regulation 2025/2501 authorises the use of protein from peas and potatoes as processing aids for the clarification of fruit juices, fruit wines, and mead. These will be included in the list of substances that may be used to produce organic products for the EU market (Regulation 2021/1165, Annex V).
EGTOP is still evaluating which substances can be authorised for cleaning and disinfection in organic production. The existing list of substances authorised specifically for cleaning and disinfecting ponds, cages, tanks, raceways, buildings, or installations for animal production (Regulation 889/2008, Annex VII) will continue to apply until 31 December 2027.
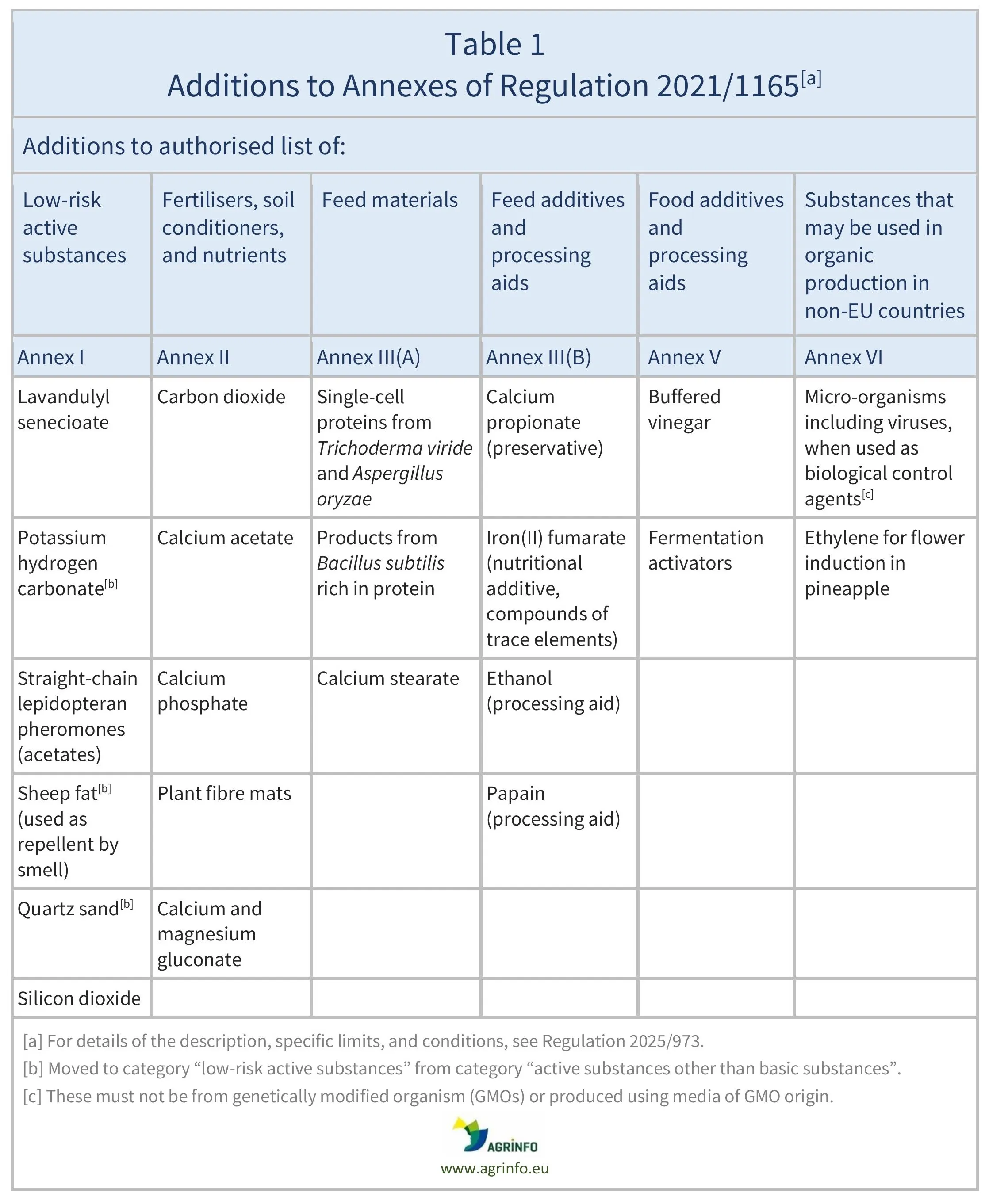
Regulation 2025/973 updates the list of substances and products that can be used to produce organic products for the EU market (see Table 1). There are additions to the lists of authorised low-risk active substances, fertilisers, feed materials, feed additives, and food additives (Annexes to Regulation 2021/1165). In particular, the following are added to the list of substances that may be used in organic production (Annex VI):
- micro-organisms, including viruses, when used as biological control agents; these must not be from genetically modified organisms (GMOs) or produced using media of GMO origin
- ethylene for flower induction in pineapple.
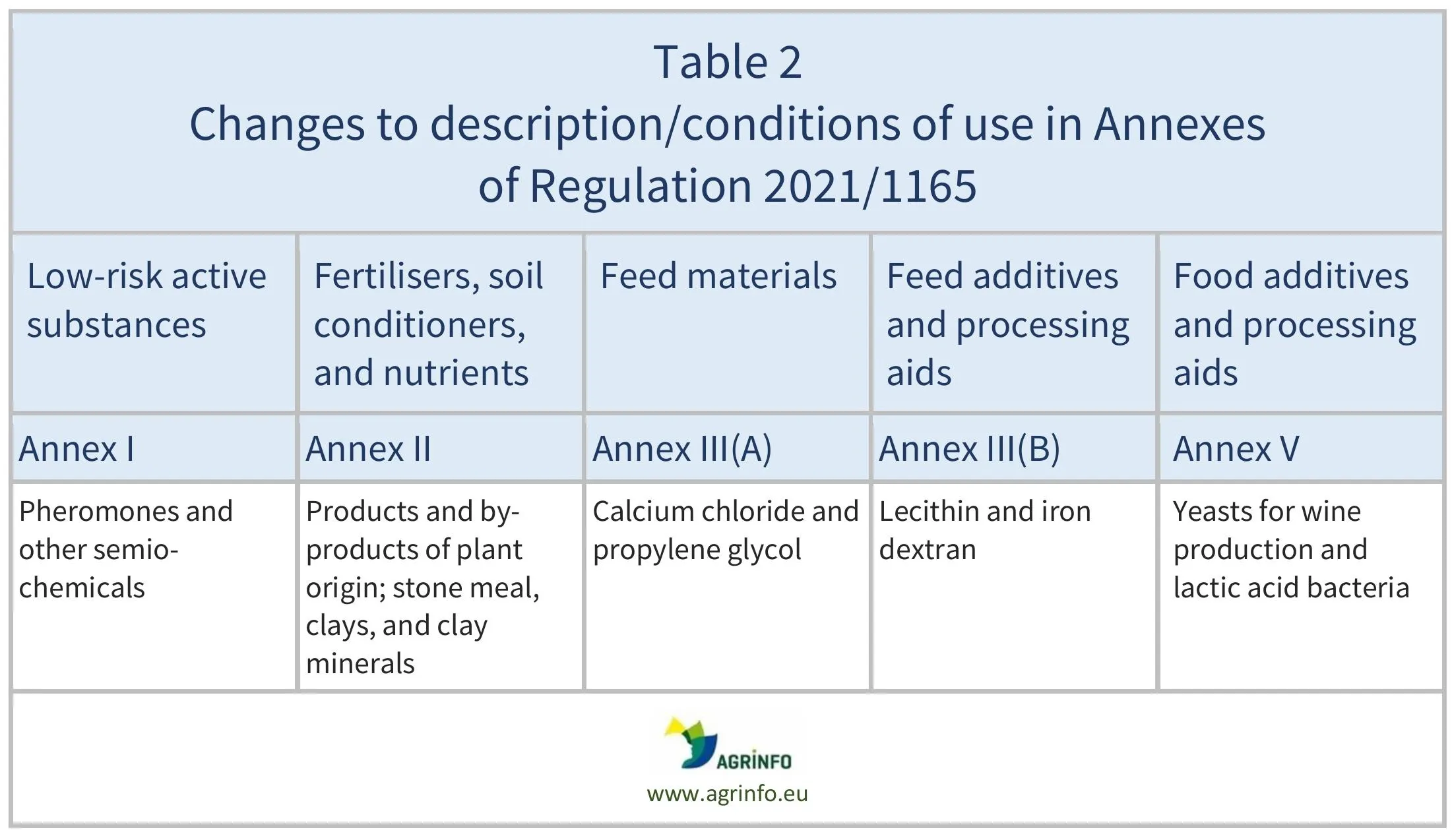
Substances where there has been an amendment to the description and/or conditions of use are summarised in Table 2.
Details of these changes can be found in the Annex to Regulation 2025/973.
Why?
The changes to the list of low-risk substances in Regulation 2025/973 reflect the renewal of approvals of these substances under Regulation 1107/2009.
The changes to fertilisers, feed additives, and the use of micro-organisms and ethylene in non-EU countries’ organic production, and the inclusion of potato and pea protein, are based on recommendations from the European Commission’s Expert Group for Technical Advice on Organic Production (see EGTOP reports on organic production).
Timeline
Regulation 2025/973 applies from 15 June 2025.
Regulation 2025/2501 applies from 1 January 2026.
Recommended Actions
Operators in non-EU countries are recommended to reconfirm with their certification body which substances are authorised for use under the new EU organic rules. Dossiers may need to be submitted to the EU in the case of some substances that were previously used under the old equivalence rules, but which now require specific EU authorisation for use on organic exports (provided they are registered for use in the country of origin).
Background
The Organic Regulation (EU) 2018/848 lays down the EU rules on organic production and labelling of organic products. It revised and strengthened the controls system, trade regime, and production rules that had been in place since 2007. The move from the principle of equivalence to the principle of conformity marked a fundamental change to the regulatory approach. The earlier Regulation (EC) 834/2007 recognised that organic goods could be produced in ways that were different, but equivalent in terms of their outcome and alignment with organic principles. Under the new Regulation, producers in non-EU countries that do not have equivalence recognised in a trade agreement with the EU, or are not recognised as an equivalent country under Regulation 834/2007, will have to conform with exactly the same set of rules as those in the EU.
In certain instances, farmers in non-EU countries, with specific conditions that are different from EU production conditions, will require different tools. Recognised control authorities/bodies can ask the Commission to evaluate and authorise additional substances in non-EU countries for use in the production of organic products for the EU market (Regulation 2021/1165, Art. 10).
For further information see New EU Organic Regulation explained.
Resources
Commission Regulation 2018/848 on organic production and labelling of organic products
Commission Regulation 2021/1165 authorising certain products and substances for use in organic production and establishing their lists
Commission Regulation 2023/2229 amending and correcting Regulation 2021/1165 authorising certain products and substances for use in organic production and establishing their lists
Commission Regulation 889/2008 laying down detailed rules on organic production and labelling of organic products with regard to organic production, labelling and control [repealed, but Annex VII still relevant]
European Commission: EGTOP reports on organic production
Sources
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
EU authorises pea/potato protein and delays review of disinfectants
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2025/2501 as regards the use of certain products and substances in organic production
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2025/973 authorising certain products and substances for use in organic production and establishing their lists
What is changing and why?
The European Union (EU) has authorised the use of protein from peas and potatoes for the organic production of fruit juices, fruit wines, and mead. This authorisation is based on recommendations from the European Commission’s Expert Group for Technical Advice on Organic Production (EGTOP). These will be included in the list of substances that may be used in the production of organic products for the EU market (Regulation 2021/1165, Annex V).
Substances currently authorised for cleaning and disinfection of buildings and installations for animal production (Regulation 889/2008, Annex VII) can be used until 31 December 2027 because EGTOP’s evaluation of these substances has been delayed.
In July 2025, the Commission updated the list of substances and products that can be used in organic products imported into the EU, adding to the list of low-risk active substances, authorised fertilisers, feed materials, feed additives, and food additives (see Tables 1 and 2).
This includes permitted use in non-EU countries of micro-organisms (including viruses) as biological control agents in organic production, and ethylene for flower induction in pineapple.
Permitting the use of ethylene in organic pineapple production and micro-organisms in organic production is expected to support organic production in non-EU countries.
Actions
Operators in non-EU countries are recommended to reconfirm with their certification body which substances are authorised for use under the new EU organic rules. Dossiers may need to be submitted to the EU in the case of some substances that were previously used under the old equivalence rules, but which now require specific EU authorisation for use on organic exports (provided they are registered for use in the country of origin).
Timeline
Regulation 2025/973 applies from 15 June 2025.
Regulation 2025/2501 applies from 1 January 2026.
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.