Plant health interceptions (EUROPHYT) in June 2025
- Plant health
- Plant health certification
- Priority pests
Summary
This report summarises EUROPHYT interceptions of products entering the European Union from low- and middle-income countries that occurred in June 2025.
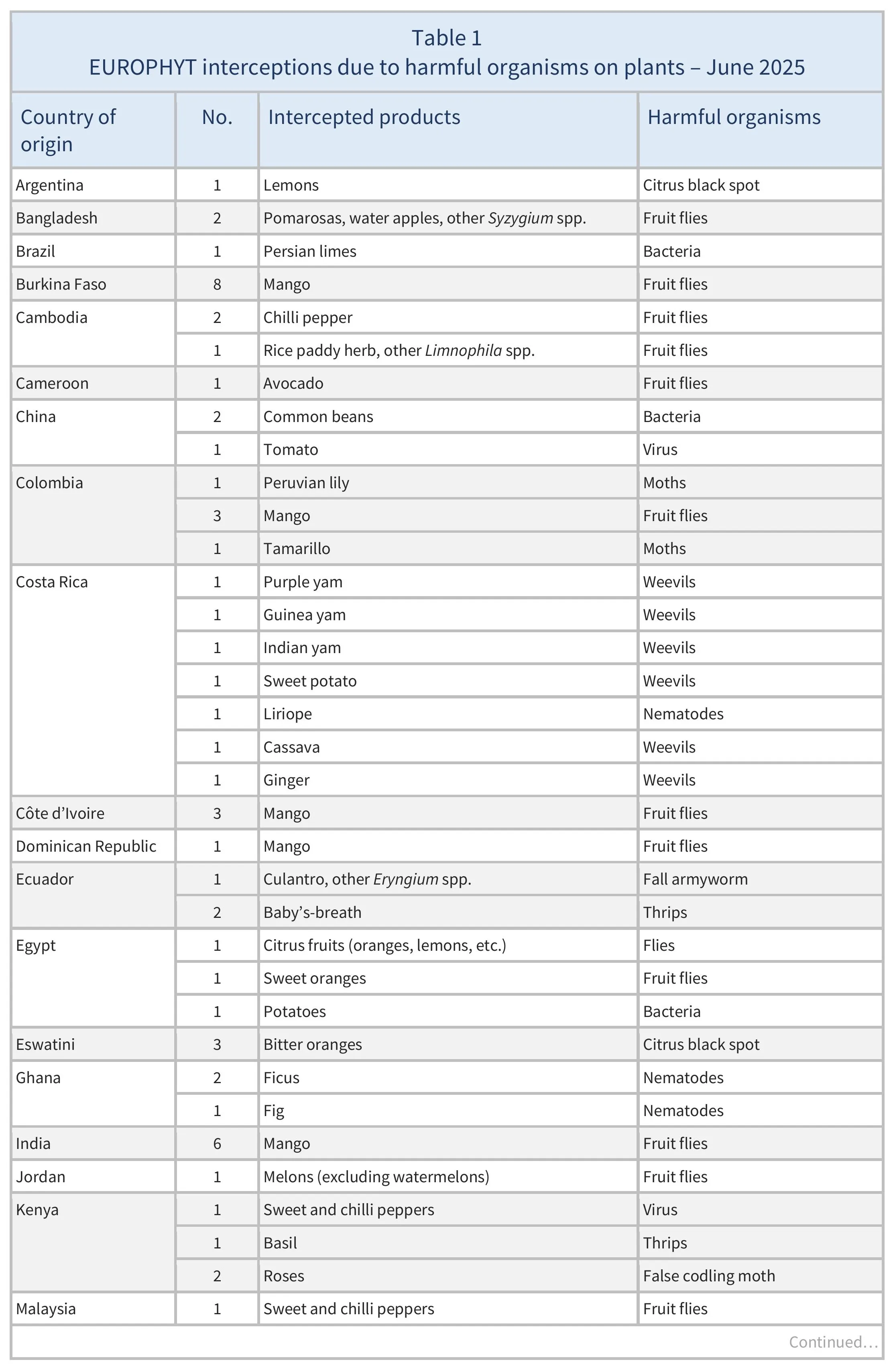
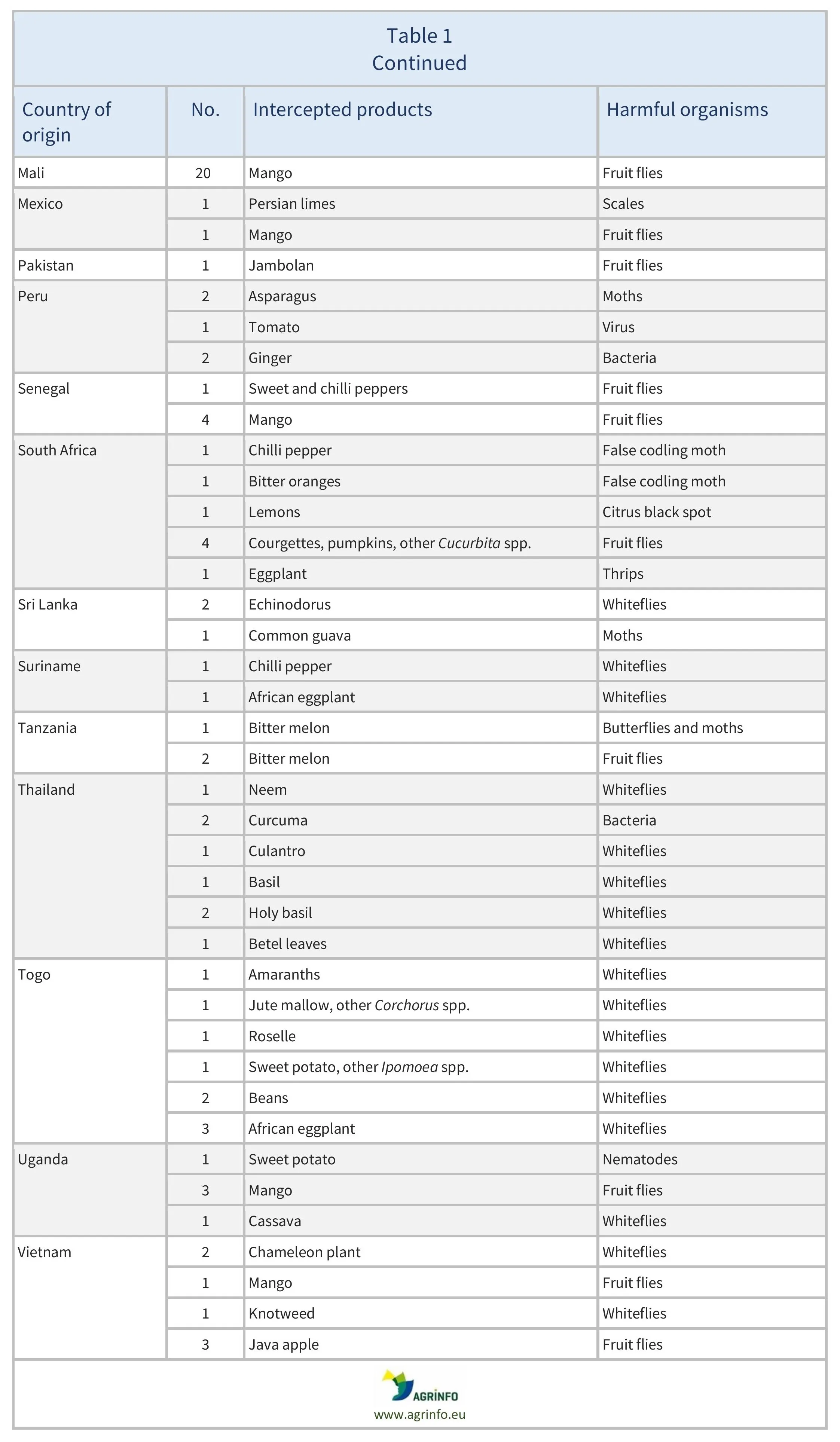
In June 2025, there were 137 interceptions of harmful organisms involving 32 AGRINFO partner countries, and 773 interceptions of other non-conformities that involved 51 partner countries.
June 2025 saw 137 interceptions of harmful organisms involving 32 AGRINFO partner countries, and 773 interceptions of other non-conformities involving 51 partner countries
TRACES: Number of occurrences of harmful organism(s) in commodities imported into the EU or Switzerland (June 2025)
Update
This report summarises EUROPHYT interceptions of products entering the European Union from low- and middle-income countries that occurred in June 2025.
In June 2025, there were 137 interceptions of harmful organisms involving 32 AGRINFO partner countries, and 773 interceptions of other non-conformities that involved 51 partner countries.
INTERCEPTIONS
Harmful organisms
In June 2025 there were 137 EUROPHYT interceptions of harmful organisms involving 32 low- and middle-income (AGRINFO partner) countries (see Table 1).
Other non-conformities
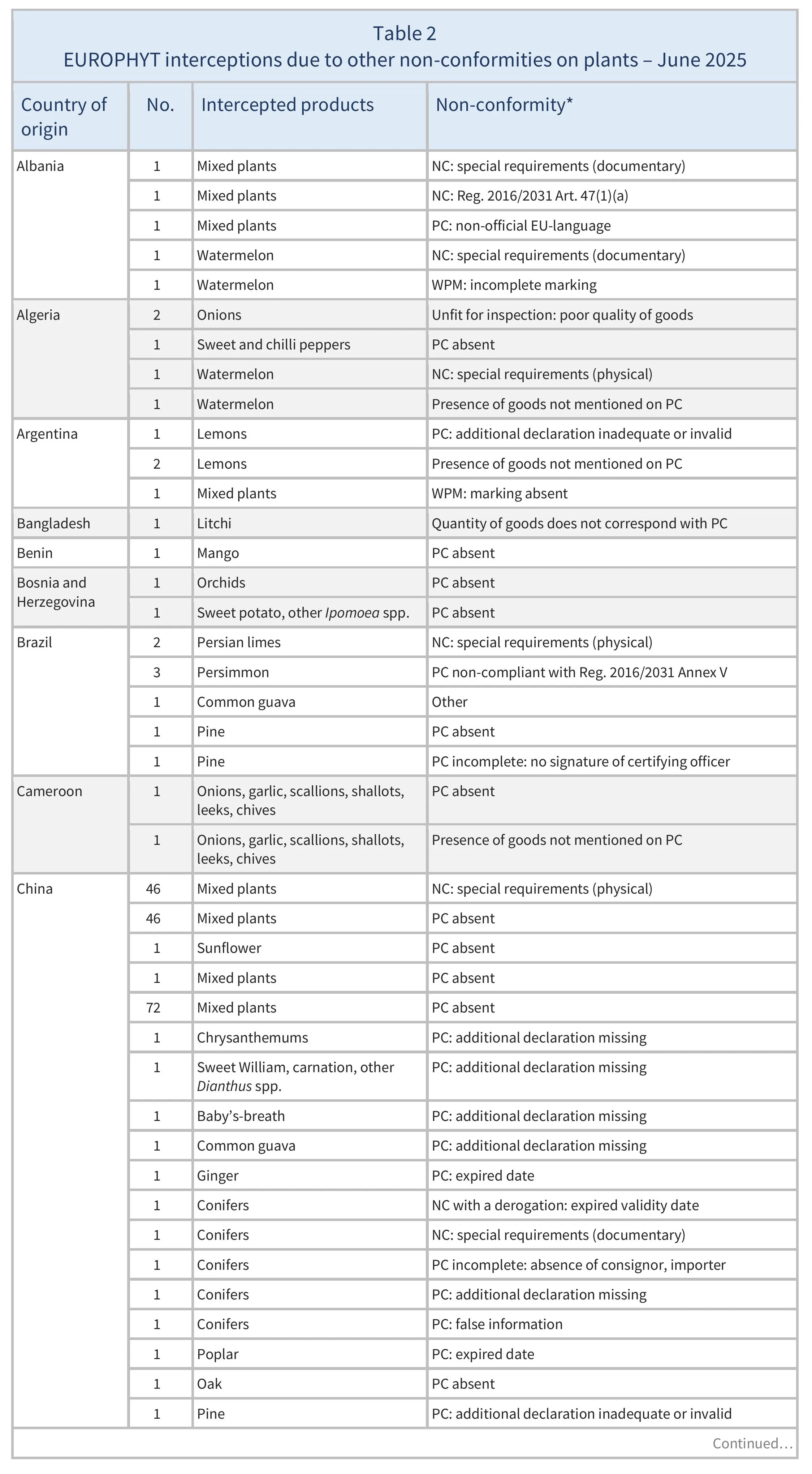
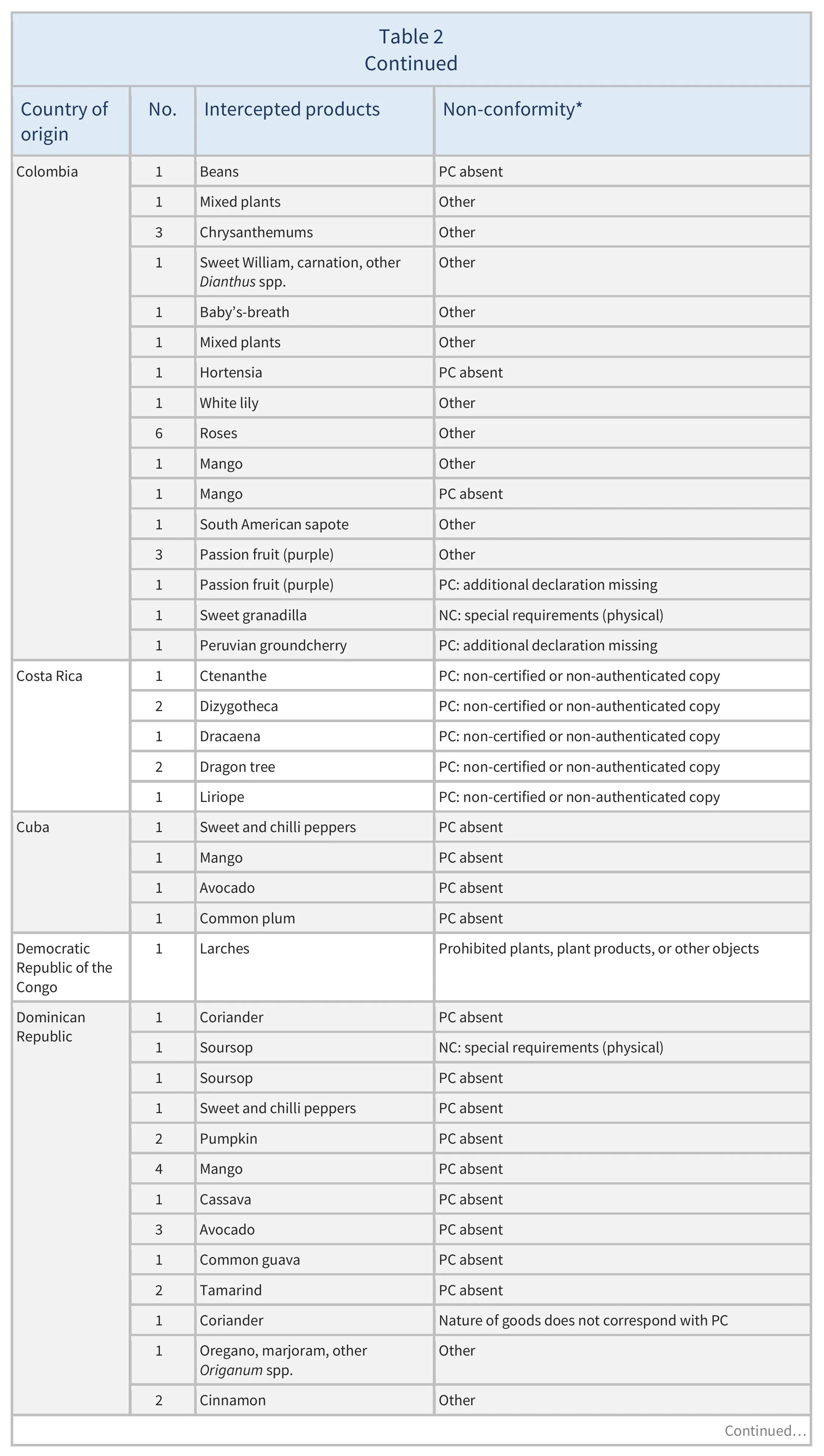
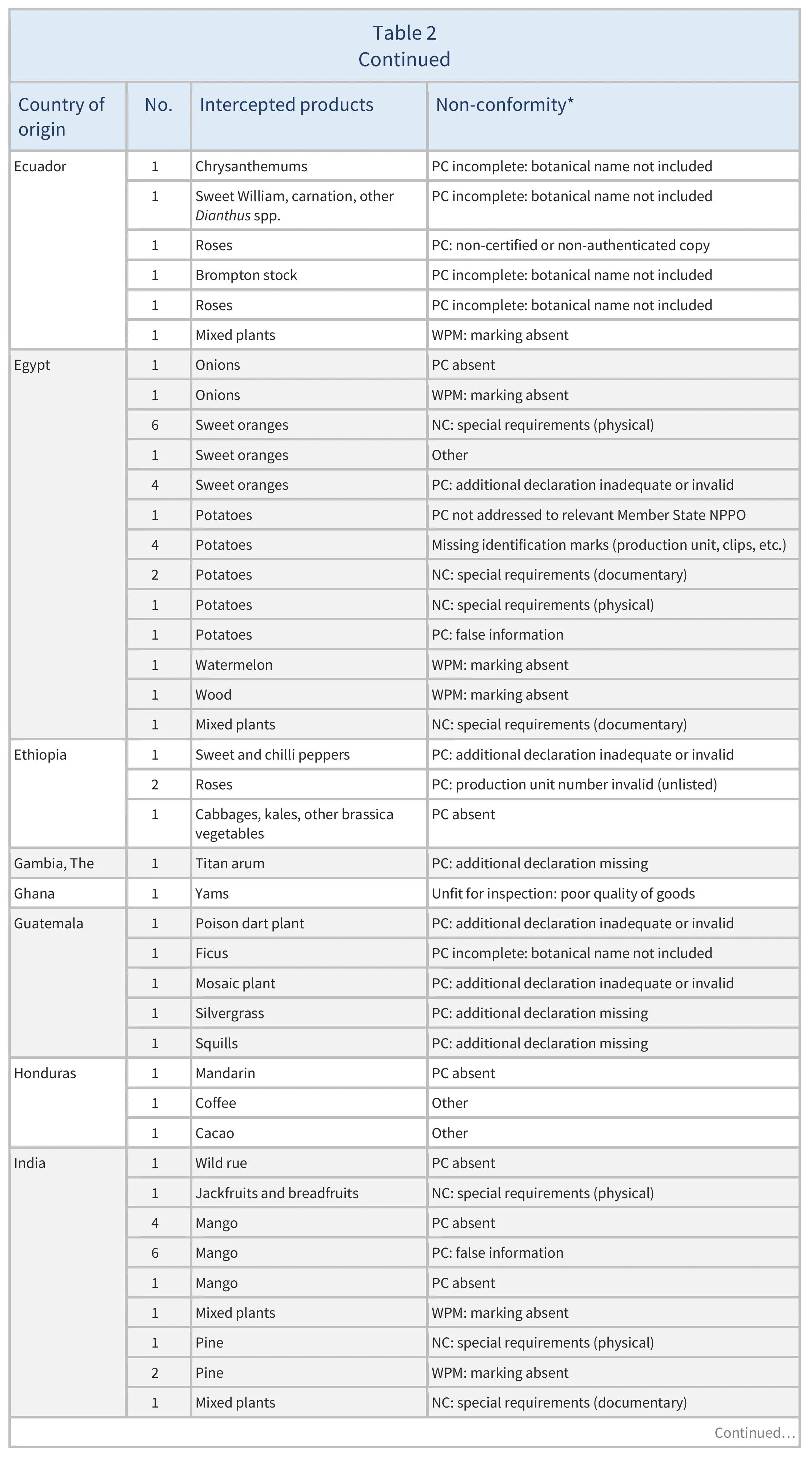
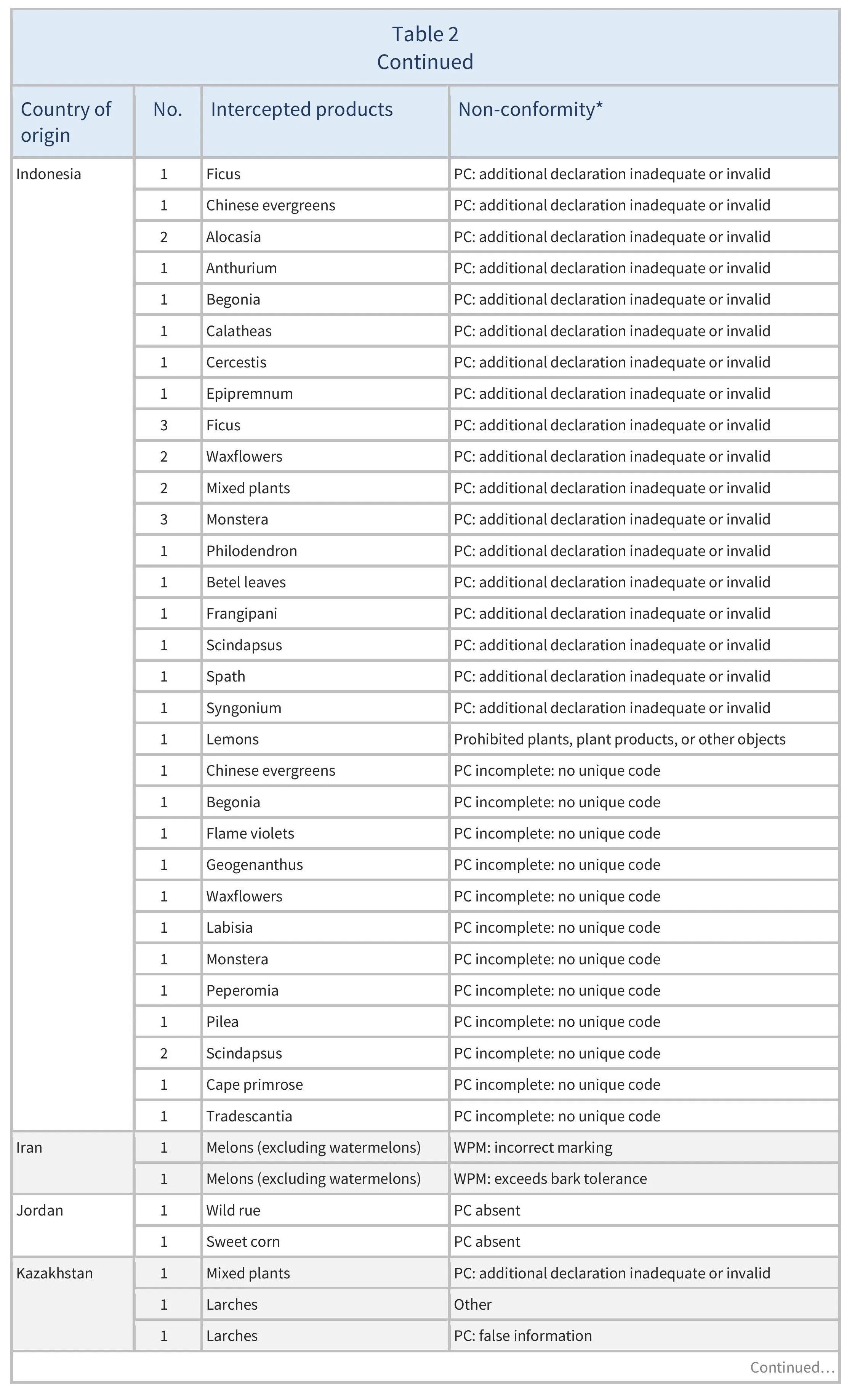
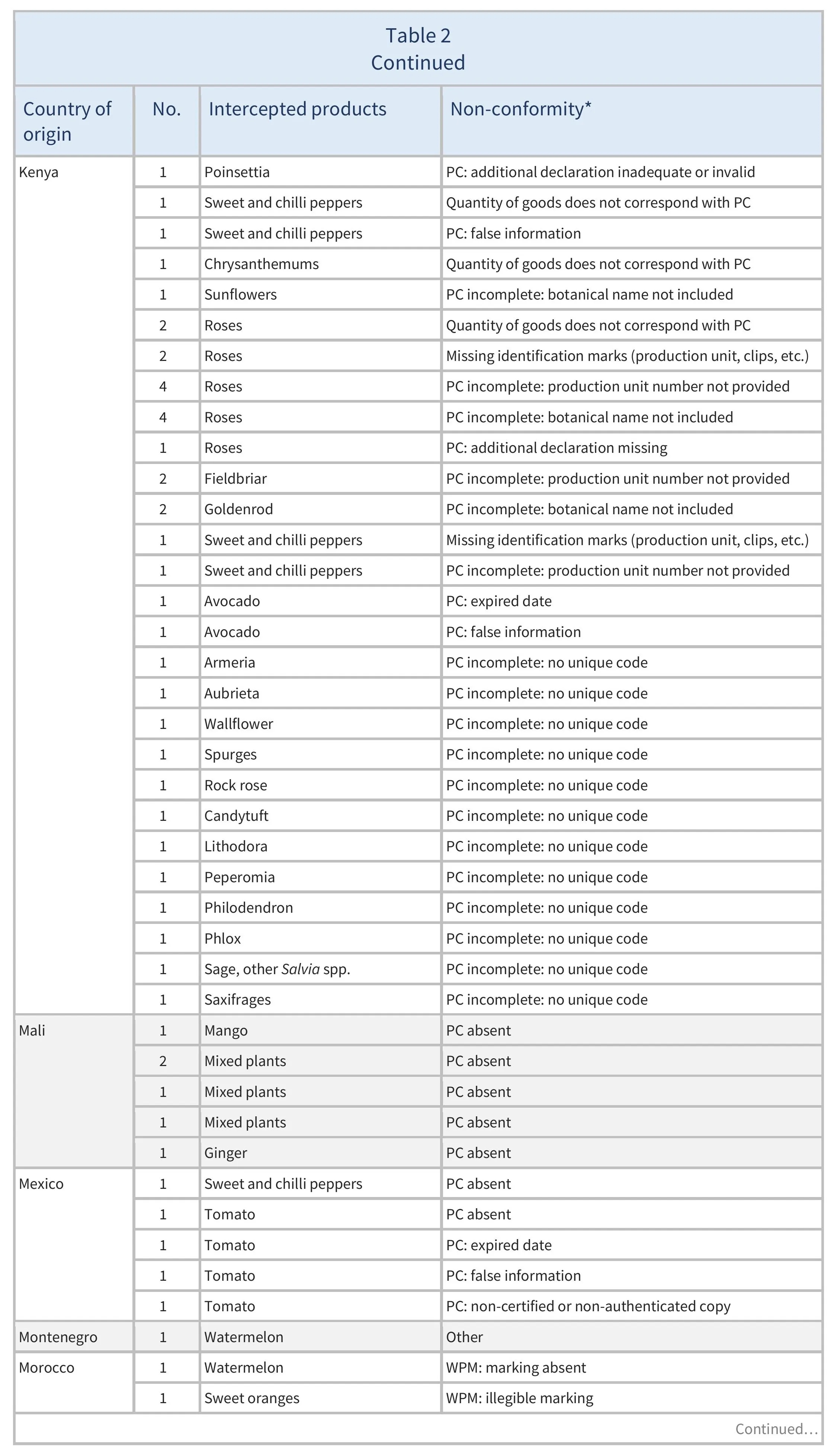
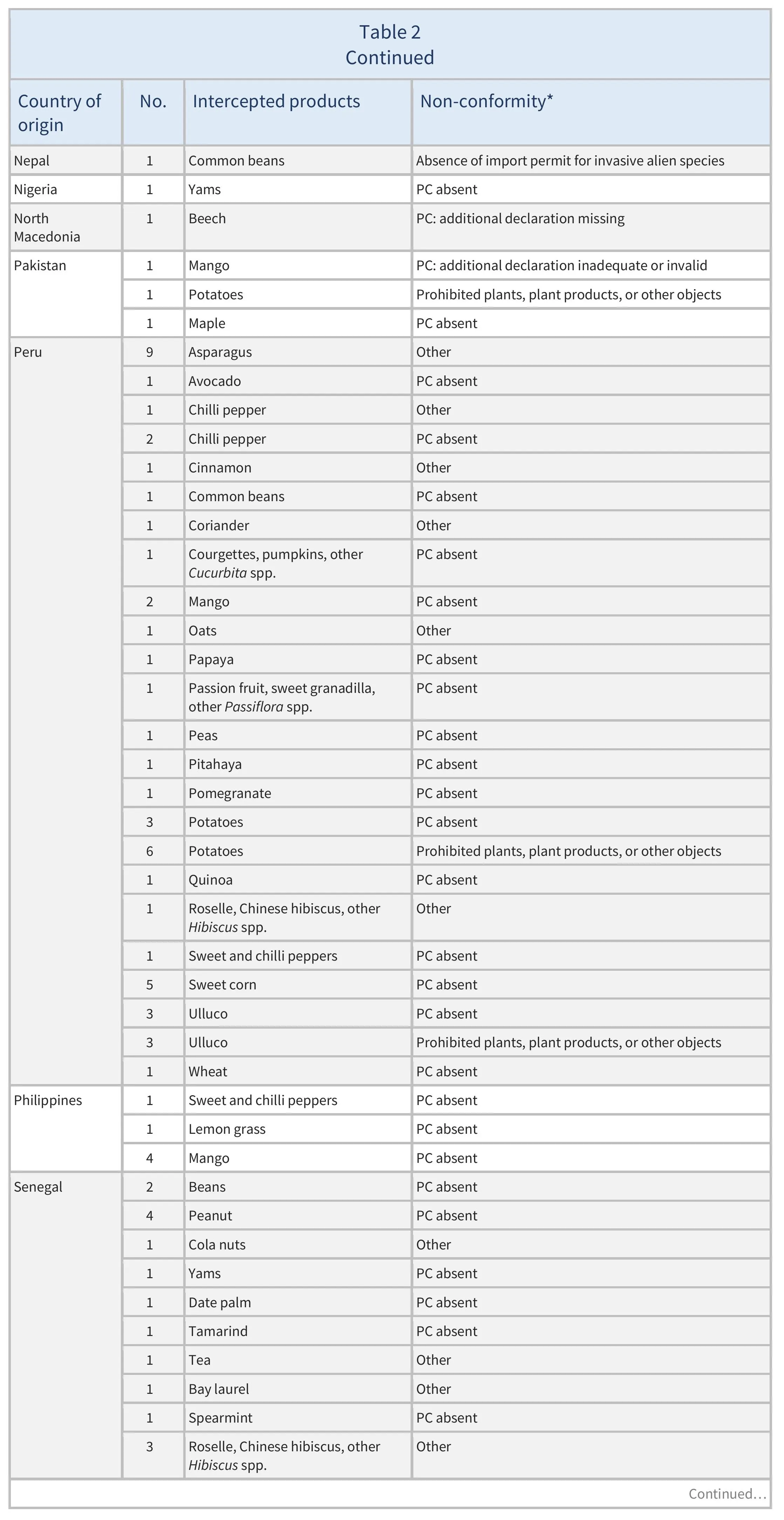
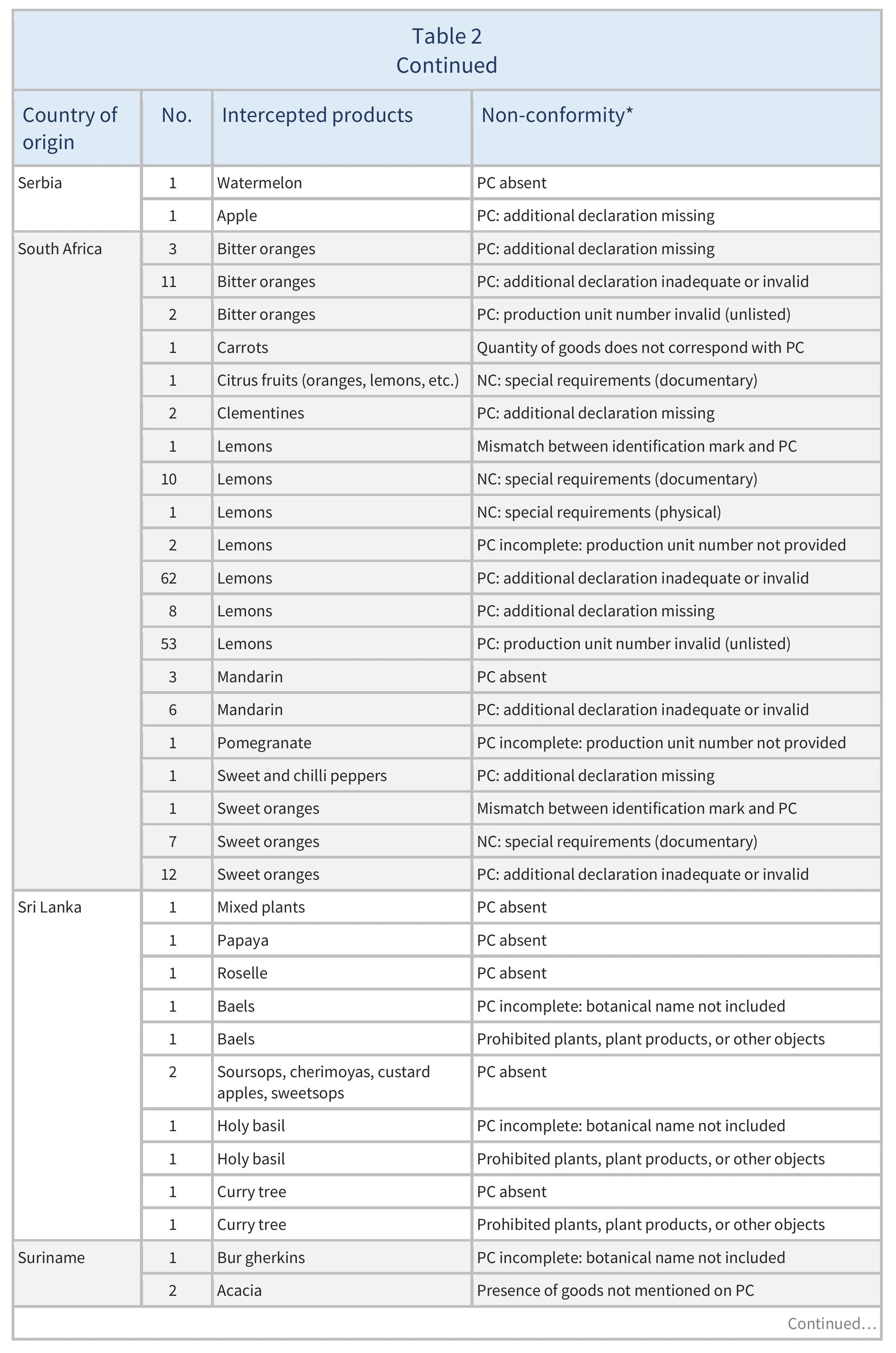
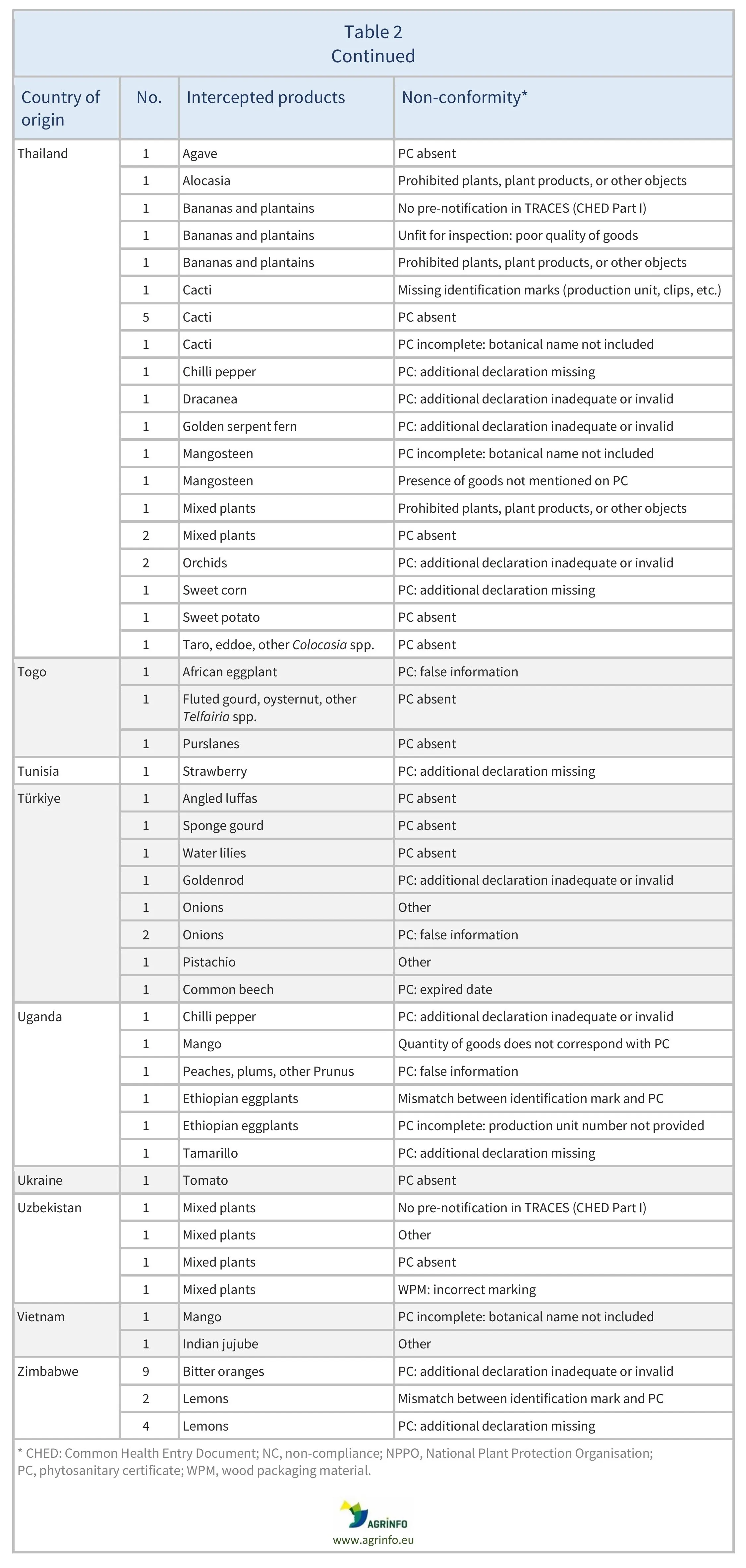
There were also 773 interceptions of other non-conformities involving 51 partner countries (see Table 2).
For more detail see TRACES: Number of occurrences of harmful organism(s) in commodities imported into the EU or Switzerland (June 2025).
Timeline
June 2025
What are the major implications for exporting countries?
EUROPHYT interceptions can have significant impacts on producers and exporters. A shipment is intercepted at EU border controls when products do not comply with the EU’s phytosanitary requirements. As a result, the affected importer/ exporter/ producer may face a range of consequences, including delayed shipments, additional costs of testing and inspection, and potential rejections or destruction of their products. These interceptions can also damage the reputation of the producer/ exporter in the EU market, which may affect their ability to conduct future trade with EU buyers. It can also have impacts on the export sector as a whole, particularly when repeated interceptions lead to more stringent plant health measures or bans.
Recommended Actions
To avoid the risk of interceptions, producers and exporters must take proactive measures to ensure their products comply with EU phytosanitary requirements. This can include implementing effective pest management strategies, using certified seeds and planting material, and complying with regulations and standards.
Background
EUROPHYT is the European Union Notification System for Plant Health Interceptions.
The basis for EUROPHYT interceptions is the obligation for EU Member States (and Switzerland) to rapidly report the occurrence of harmful organisms and other non-conformities found during import controls, to prevent the introduction and spread of pests and diseases. Interceptions of “other non-conformities” are usually caused by an inaccurate or missing phytosanitary certificate.
Notifications of such interceptions are disseminated EU-wide and to the National Plant Protection Organisation (NPPO) of the exporting country. The legal framework for EUROPHYT interceptions is provided by Regulation 2016/2031 on plant health. For more information about plant health law, see EU Plant Health Law explained.
Also see Official Controls Regulation - explained.
Resources
European Plant Protection Organization (EPPO)
European Commission (2024) Interceptions of harmful organisms in imported plants and other objects
Sources
TRACES: Number of occurrences of harmful organism(s) in commodities imported into the EU or Switzerland (June 2025)
Tables & Figures
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
June 2025 saw 137 interceptions of harmful organisms involving 32 AGRINFO partner countries, and 773 interceptions of other non-conformities involving 51 partner countries
TRACES: Number of occurrences of harmful organism(s) in commodities imported into the EU or Switzerland (June 2025)
INTERCEPTIONS
This report summarises plant health (EUROPHYT) interceptions of products entering the European Union (EU) from low- and middle-income countries that occurred in June 2025.
There were 137 EUROPHYT interceptions of harmful organisms involving 32 AGRINFO partner countries (see Table 1), and 773 interceptions of other non-conformities involving 51 partner countries (see Table 2).
Shipments are intercepted at EU border controls when products do not comply with the EU’s phytosanitary requirements. EUROPHYT reports the presence of harmful organisms and other non-conformities found during inspections. Interceptions of “other non-conformities” are usually caused by an inaccurate or missing phytosanitary certificate.
EUROPHYT interceptions can have significant impacts on importers, exporters, and producers. Those affected may face delayed shipments, additional costs of testing and inspection, and potential rejections or destruction of their products, as well as reputational damage.
Actions
To avoid the risk of interceptions, producers and exporters must take proactive measures to ensure their products comply with EU phytosanitary requirements. This can include implementing effective pest management strategies, using certified seeds and planting material, and complying with regulations and standards.
Timeline
June 2025
Tables & Figures
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.