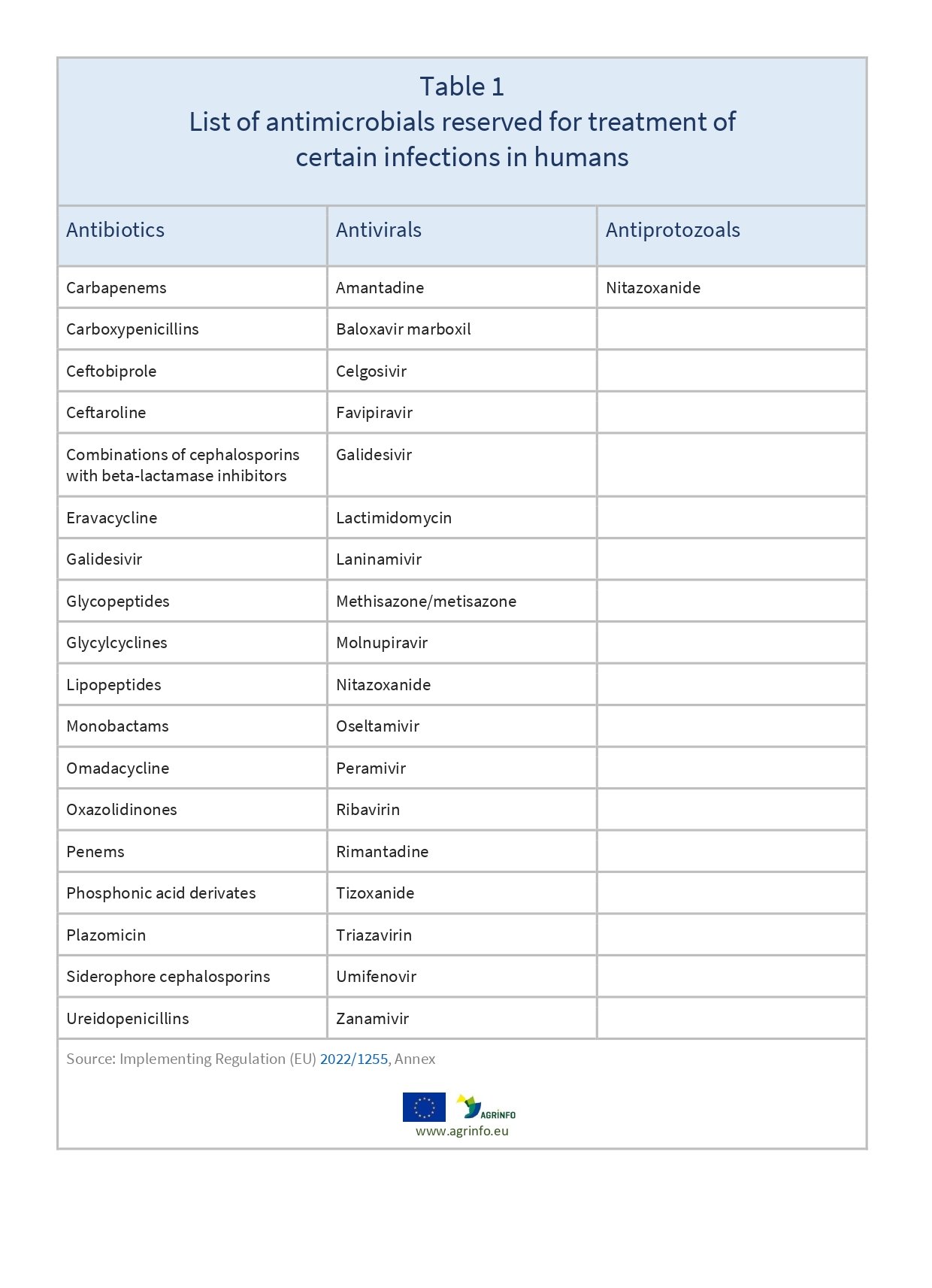
List of antimicrobials reserved for treatment of certain infections in humans
- Antimicrobial resistance
Summary
The EU published the list of antimicrobials (antibiotics, antivirals, and antiprotozoals) that must be limited to human use and cannot be used on animals. From 3 September 2026, only foods produced from animals that have never been treated with these substances will be authorized to be exported to the EU (see Rules on prohibited antimicrobials in imported animal products).
The antimicrobials listed (antibiotics, antivirals, antiprotozoals) can only be for human use and must not be used on food-producing animals
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2022/1255 of 19 July 2022 designating antimicrobials or groups of antimicrobials reserved for treatment of certain infections in humans, in accordance with Regulation (EU) 2019/6 of the European Parliament and of the Council
Update
The EU published the list of antimicrobials (antibiotics, antivirals, and antiprotozoals) that must be limited to human use and cannot be used on animals. From 3 September 2026, only foods produced from animals that have never been treated with these substances will be authorized to be exported to the EU (see Rules on prohibited antimicrobials in imported animal products).
What is changing?
The EU now prohibits the use in food-producing animals of the substances listed in Table 1.
Why?
Antimicrobial resistance is viewed as a major threat to global health. The EU seeks to limit the use of certain drugs to treat humans, to ensure their continued efficiency. This is consistent with the EU’s One Health Approach: “antimicrobial management in one sector may affect antimicrobial resistance in the other sectors” [Delegated Regulation (EU) 2021/1760, recital (2)].
Timeline
The list applies from 9 February 2023 for food of animal origin produced in the EU and from 3 September 2026 for food of animal origin exported from non-EU countries to the EU (Regulation 2023/905).
What are the major implications for exporting countries?
If these antimicrobials are used in exporting countries in food-producing animals (or their products) intended for export to the EU, their use must be identified and replaced by alternatives.
Recommended Actions
Exporters of animals and of foods of animal origin must ensure that foods that enter the EU from 3 September 2026 are produced from animals that have not been treated with one of the listed antimicrobial treatments (even for medical use).
Background
In the framework of the fight against antimicrobial resistance, Regulation (EU) 2019/6 sets a range of concrete measures to fight antimicrobial resistance and to promote more prudent and responsible use of antimicrobial medicinal products in animals, including very strict rules on their veterinary prescription for prophylactic and metaphylactic use. That Regulation also states that antimicrobial medicinal products should not be administered routinely, or used to compensate for poor hygiene, inadequate animal husbandry, lack of care or poor farm management. Art. 118(1) foresees that the obligation will also apply to foods of animal origin exported to the EU.
Delegated Regulation (EU) 2021/1760 establishes criteria for the designation of antimicrobials to be reserved for treatment of certain infections in humans. Based on these criteria, Implementing Regulation (EU) 2022/1255 now lays down this list of antimicrobials.
Sources
Implementing Regulation (EU) 2022/1255
Tables & Figures
.
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
The antimicrobials listed (antibiotics, antivirals, antiprotozoals) can only be for human use and must not be used on food-producing animals
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2022/1255 designating antimicrobials or groups of antimicrobials reserved for treatment of certain infections in humans, in accordance with Regulation (EU) 2019/6 of the European Parliament and of the Council
What is changing and why?
Antimicrobial resistance is viewed as a major threat to global health. The EU seeks to limit the use of certain drugs to treat humans, to ensure their continued efficiency. The EU now prohibits the use of the substances listed in Table 1 in food-producing animals.
Actions
Exporters of animals and of foods of animal origin must ensure that foods that enter the EU from 3 September 2026 are produced from animals that have not been treated with any of the listed antimicrobial treatments (even for medical use) (see Rules on prohibited antimicrobials in imported animal products).
Timeline
The list applies from 9 February 2023 for food of animal origin produced in the EU and from 3 September 2026 for food of animal origin exported from non-EU countries to the EU (Regulation 2023/905).
Tables & Figures

.
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
