Latest novel food authorisations, amendments, and extensions 2024
- Food safety
- Novel/traditional foods
Summary
This report summarises recent EU decisions to authorise, amend, or extend the specifications or conditions of use of existing novel foods:
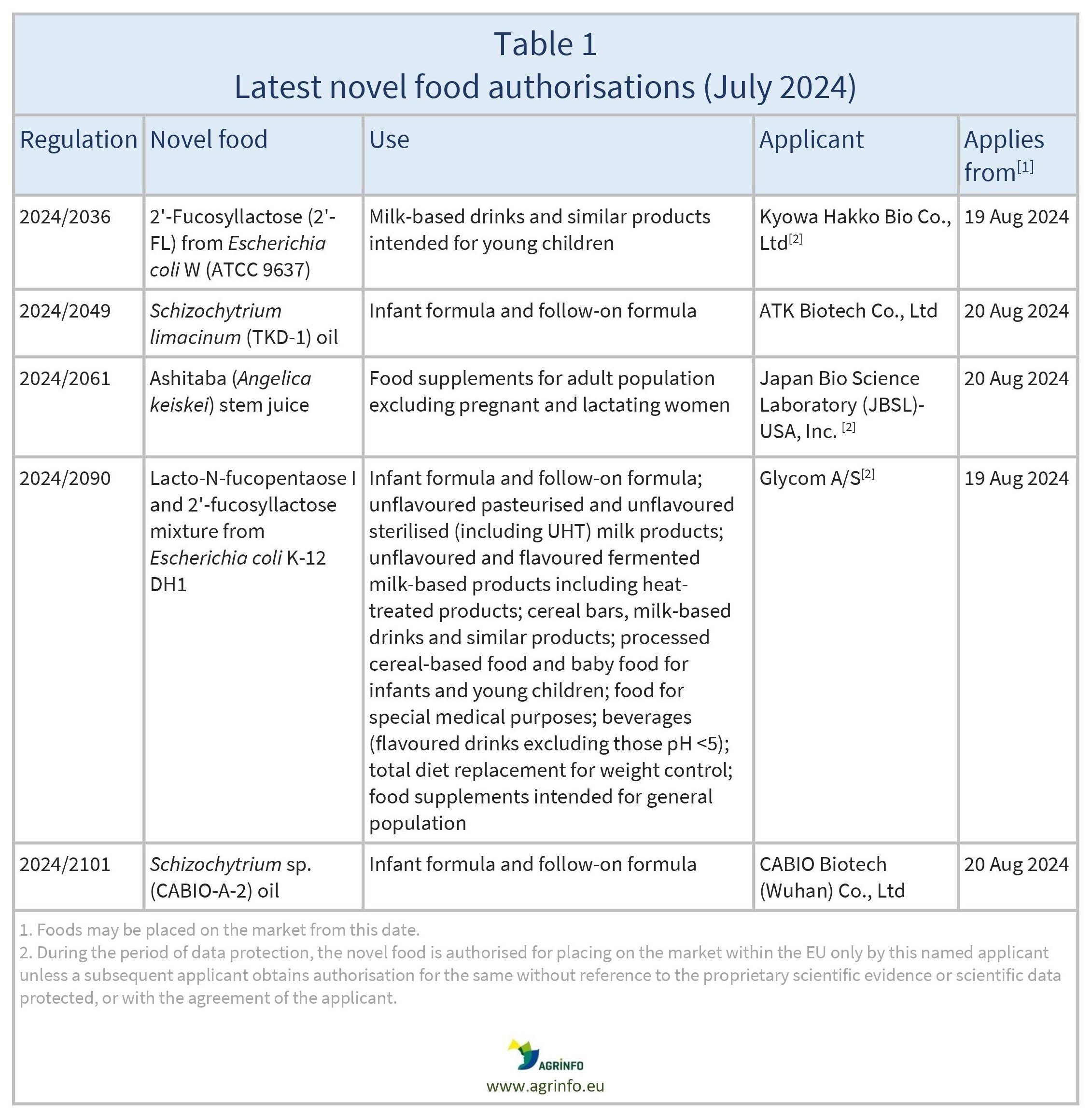
- 2'-FL obtained by microbial fermentation using a derivative strain of Escherichia coli by Kyowa Hakko Bio Co.
- LNFP-I/2'-FL mixture obtained by microbial fermentation using a derivative strain of E. coli
- Schizochytrium limacinum (TKD-1) oil
- Schizochytrium sp. (CABIO-A-2) oil
- Ashitaba stem juice.
The EU has authorised the following changes:
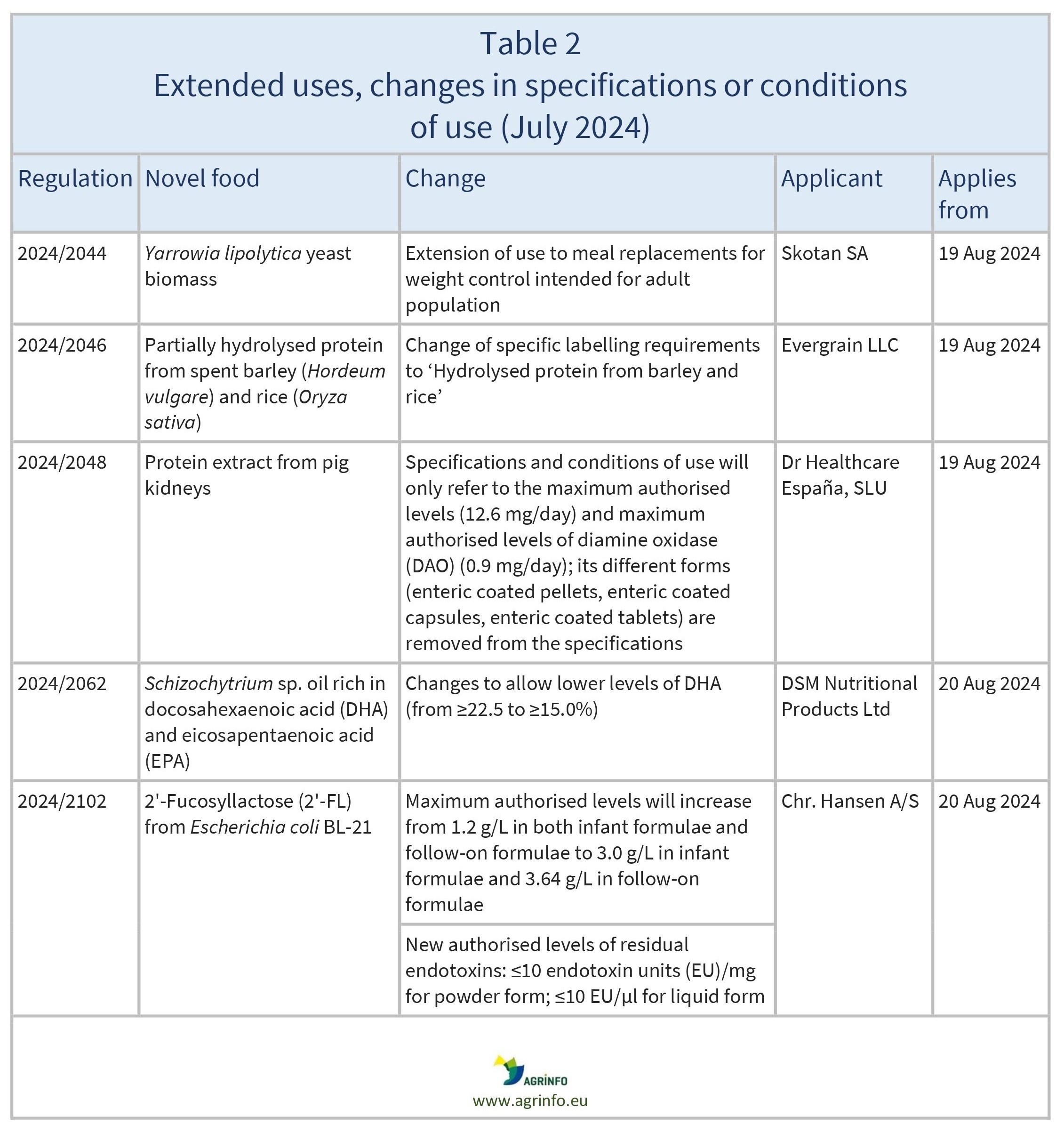
- extension of use of the novel food Yarrowia lipolytica yeast biomass to meal replacements for weight control intended for the adult population
- labelling requirements ‘Partially hydrolysed protein from barley and rice’ for foods containing partially hydrolysed protein from spent barley and rice
- specifications and conditions of use of protein extract from pig kidneys will only refer to the maximum authorised levels; its different forms are removed from the specifications
- lower levels of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in specifications of the novel food Schizochytrium sp. oil rich in DHA and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- authorised levels of 2'-FL will increase from current levels authorised in both infant formulae and follow-on formulae
- authorised levels of residual endotoxins for 2'-FL produced from derivative strain E. coli BL-21 will be aligned to levels already authorised under the same conditions of use for 2'-FL from E. coli K-12, and other milk oligosaccharides at similar residual levels in infant formulae and follow-on formulae.
Novel food authorisations, amended uses, and extensions adopted January–July 2024
Authorisations
Commission Implementing Regulations 2024/2036, 2024/2049, 2024/2061, 2024/2090, 2024/2101
Amendments
Commission Implementing Regulations 2024/2044, 2024/2046, 2024/2048, 2024/2062, 2024/2102
Update
This report summarises recent EU decisions to authorise, amend, or extend the specifications or conditions of use of existing novel foods:
- 2'-FL obtained by microbial fermentation using a derivative strain of Escherichia coli by Kyowa Hakko Bio Co.
- LNFP-I/2'-FL mixture obtained by microbial fermentation using a derivative strain of E. coli
- Schizochytrium limacinum (TKD-1) oil
- Schizochytrium sp. (CABIO-A-2) oil
- Ashitaba stem juice.
The EU has authorised the following changes:
- extension of use of the novel food Yarrowia lipolytica yeast biomass to meal replacements for weight control intended for the adult population
- labelling requirements ‘Partially hydrolysed protein from barley and rice’ for foods containing partially hydrolysed protein from spent barley and rice
- specifications and conditions of use of protein extract from pig kidneys will only refer to the maximum authorised levels; its different forms are removed from the specifications
- lower levels of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in specifications of the novel food Schizochytrium sp. oil rich in DHA and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- authorised levels of 2'-FL will increase from current levels authorised in both infant formulae and follow-on formulae
- authorised levels of residual endotoxins for 2'-FL produced from derivative strain E. coli BL-21 will be aligned to levels already authorised under the same conditions of use for 2'-FL from E. coli K-12, and other milk oligosaccharides at similar residual levels in infant formulae and follow-on formulae.
Impacted Products
Milk products (pasteurised, sterilised, UHT), fermented milk-based products, flavoured beverages, cereal bars, infant formula, follow-on formula, processed cereal-based food and baby food, diet replacement foods (for weight control), special medical foods, food supplements
What is changing?
The European Commission has authorised the novel foods listed in Table 1 to be placed on the EU market. These foods will be included in the Union list of novel foods (Regulation 2017/2470). For certain novel foods, only the company applicants that were granted authorisation are permitted to sell them on the EU market over the next 5 years, unless they permit other companies to sell them, or if another company obtains a novel food authorisation without reference to the protected scientific data used by the original applicant (see footnote to Table 1).
The Commission has also authorised some changes to the specifications and conditions of use for certain novel foods that are already authorised and available on the EU market (see Table 2).
Why?
Only novel foods authorised and included in the Union list of novel foods may be placed on the market within the EU (Regulation 2015/2283).
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) evaluates novel food applications to ensure their safety under the proposed conditions and/or levels of use [see Resources 1–6].
Timeline
The newly authorised novel foods may be placed on the EU market from the date indicated in Table 1.
Changes to specifications and conditions apply from the dates shown in Table 2.
Background
For further information on the novel food authorisation process, see Novel foods explained.
Resources
European Commission: Union list of novel foods
Regulation (EU) 2017/2470 (Union list of novel foods)
Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 on novel foods
Regulation No 1169/2011 on the provision of food information to consumers
Opinions published by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) on the safety/efficacy of the following novel foods:
- EFSA (2023) Safety of 2′‐fucosyllactose (2′‐FL) produced by a derivative strain (Escherichia coli SGR5) of E. coli W (ATCC 9637) as a Novel Food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA Journal, 21(11): 8333.
- EFSA (2023) Safety of the extension of use of 2′-fucosyllactose (2′-FL) as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA Journal, 21(11): e8334.
- EFSA (2023) Safety of an extension of use of Yarrowia lipolytica yeast biomass as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA Journal, 21(11): e8416.
- EFSA (2023) Safety of lacto-N-fucopentaose I/2’-fucosyllactose (LNFP-I/2’-FL) mixture as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA Journal, 21(12): e8412.
- EFSA (2023) Safety of oil from Schizochytrium limacinum (strain TKD‐1) for use in infant and follow‐on formula as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA Journal, 21(12): e8414.
- EFSA (2023) Safety of oil from Schizochytrium sp. (strain CABIO‐A‐2) for use in infant and follow‐on formula as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA Journal, 21(12): e8415.
Sources
Commission Implementing Regulations:
2024/2036 authorising the placing on the market of 2'-Fucosyllactose produced by a derivative strain of Escherichia coli W (ATCC 9637) as a novel food
2024/2044 as regards the specifications and the conditions of use of the novel food Yarrowia lipolytica yeast biomass
2024/2046 as regards the specific labelling requirements for the novel food partially hydrolysed protein from spent barley (Hordeum vulgare) and rice (Oryza sativa)
2024/2048 as regards the specifications and the conditions of use of the novel food protein extract from pig kidneys
2024/2049 authorising the placing on the market of Schizochytrium limacinum (TKD-1) oil as a novel food
2024/2061 authorising the placing on the market of the juice of the stems of the Angelica keiskei plant (Ashitaba stem juice) as a novel food
2024/2062 as regards the specifications of the novel food Schizochytrium sp. oil rich in DHA and EPA
2024/2090 authorising the placing on the market of Lacto-N-fucopentaose I and 2'-Fucosyllactose mixture produced using a derivative strain of Escherichia coli K-12 DH1 as a novel food
2024/2101 authorising the placing on the market of Schizochytrium sp. (CABIO-A-2) oil as a novel food
2024/2102 as regards the conditions of use of the novel food 2'-Fucosyllactose and as regards the specifications of the novel food 2'-Fucosyllactose produced with a derivative strain of Escherichia coli BL-21
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
Novel food authorisations, amended uses, and extensions adopted January–July 2024
Authorisations
Commission Implementing Regulations 2024/2036, 2024/2049, 2024/2061, 2024/2090, 2024/2101
Amendments
Commission Implementing Regulations 2024/2044, 2024/2046, 2024/2048, 2024/2062, 2024/2102
What is changing and why?
The European Commission has authorised the novel foods listed in Table 1 to be placed on the EU market.
The Commission has also authorised some changes to the specifications and conditions of use for certain novel foods that are already authorised and available on the EU market (see Table 2).
Timeline
The newly authorised novel foods may be placed on the EU market from the date indicated in Table 1.
Changes to specifications and conditions apply from the dates shown in Table 2.
Tables & Figures
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.