Maximum residue level for difenoconazole
- Pesticide MRLs
Summary
The European Union (EU) is discussing its review of the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for difenoconazole. This includes lowering the MRLs to the to the limit of determination (LOD) for certain products where information from the European Food Safety Authority was not sufficient to rule out risks for consumers. (The LOD is the lowest level that can be detected using the most modern and reliable analytical methods.)
For citrus fruits, tree nuts, mangoes, papayas, dry peas, and soyabeans, where proposed MRLs are not considered to be a concern for consumer safety, import tolerances are being discussed.
EU discusses MRLs and import tolerances for difenoconazole on various products
Draft Commission Regulation amending Annex II and III to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards maximum residue levels for difenoconazole in or on certain products [download]
Draft Annex II [download]
Update
The European Union (EU) is discussing its review of the maximum residue levels (MRLs) for difenoconazole. This includes lowering the MRLs to the to the limit of determination (LOD) for certain products where information from the European Food Safety Authority was not sufficient to rule out risks for consumers. (The LOD is the lowest level that can be detected using the most modern and reliable analytical methods.)
For citrus fruits, tree nuts, mangoes, papayas, dry peas, and soyabeans, where proposed MRLs are not considered to be a concern for consumer safety, import tolerances are being discussed.
Impacted Products
Almonds, Brazil nuts, cashew nuts, chestnuts, coconuts, hazelnuts/cobnuts, macadamias, pecans, pine kernels, pistachios, walnuts, apples, pears, quinces, medlars, loquats/Japanese medlars, cherries (sweet), plums, cranberries, azaroles/Mediterranean medlars, currants, dewberries, elderberries, gooseberries, rose hips, mulberries, American persimmons/Virginia kaki, carambolas, dates, figs, jambuls/jambolans, litchis/lychees, star apples/cainitos, kaki/Japanese persimmons, mangoes, papayas, breadfruits, cherimoyas, durians, granate apples/pomegranates, pineapples, soursops/guanabanas, guavas, passionfruits/maracujas, potatoes, sweet potatoes, cassava roots/manioc, yams, arrowroots, garlic, onions, shallots, aubergines/eggplants, sweetcorn, broccoli, cauliflowers, Chinese cabbages/pe-tsai, kales, kohlrabies, Roman rocket/rucola, spinaches, purslanes, chards/beet leaves, grape leaves, watercresses, witloofs/Belgian endives, celery leaves, chervil, parsley, basil and edible flowers, beans and peas, lentils, asparagus, cardoons, celeries, bamboo shoots, palm hearts, fungi, mosses and lichens, algae and prokaryotes, lentils, lupins/lupini beans, linseeds, mustard seeds, castor beans, hemp seeds, peanuts/groundnuts, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, soyabeans, cotton seeds, borage seeds, oil palm kernels, oil palm fruits, kapok, buckwheat and other pseudocereals, common millet/proso millet, maize/corn, sorghum, rye, wheat, oats, teas, valerian, ginseng, anise/aniseed, black caraway/black cumin, celery, coriander, cumin, dill, fennel, fenugreek, nutmeg, allspice/pimento, Sichuan pepper, caraway, cardamom, juniper berry, peppercorn, vanilla, tamarind, capers, cinnamon, cloves, mace, saffron, liquorice, turmeric/curcuma, sugar canes
What is changing?
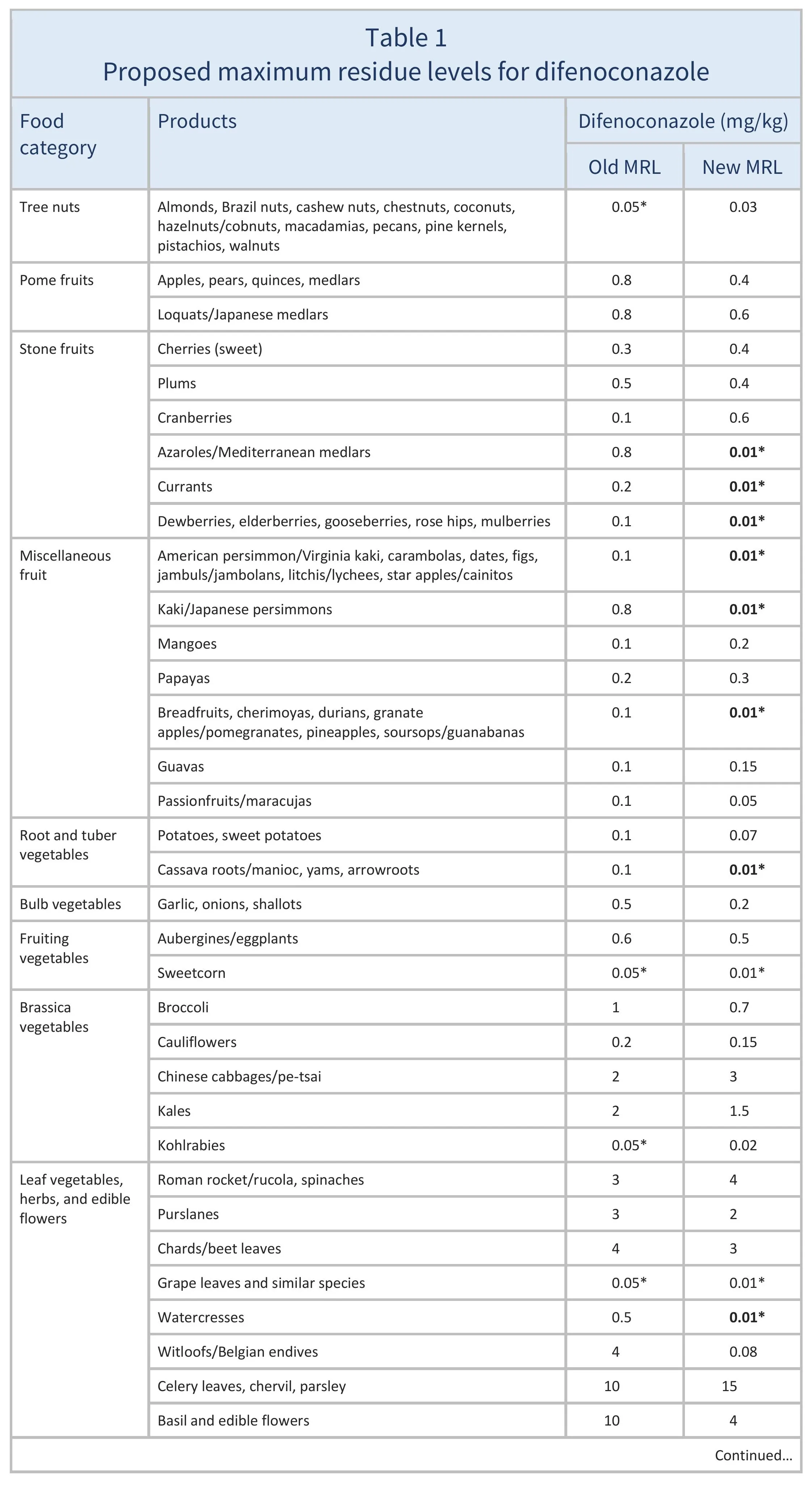
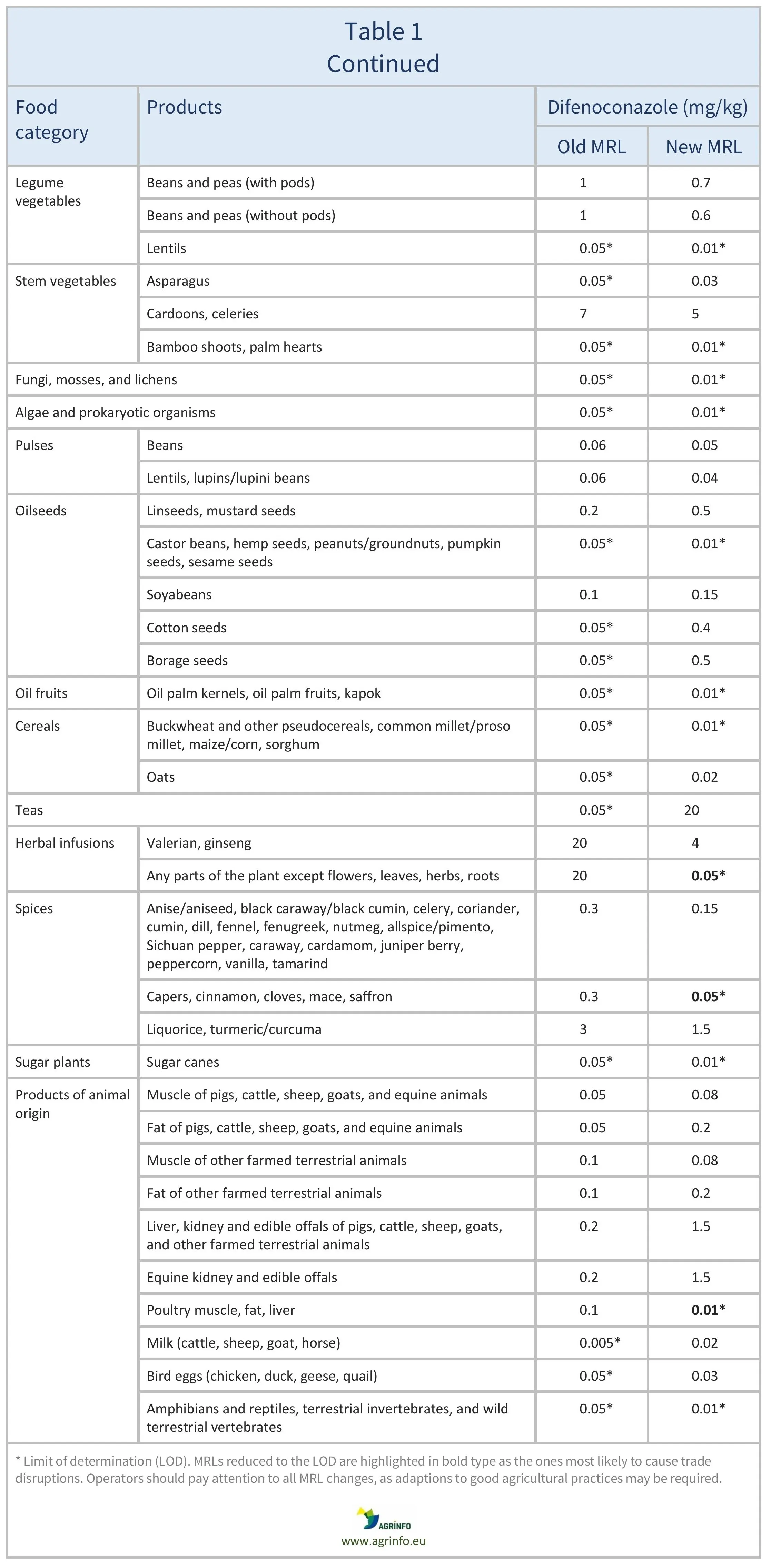
The EU is discussing amending the MRLs for difenoconazole as summarised in Table 1.
For citrus fruits, tree nuts, mangoes, papayas, dry peas, and soyabeans, where proposed MRLs are not considered to be a concern for consumer safety (EFSA 2025), import tolerances are being discussed. EFSA (2024) also recommended lowering the MRLs for potatoes, sweet potatoes, aubergines, chards, cardoons, and celeries, and derived safe MRLs for certain other crops based on good agricultural practices (GAPs).
Why?
In 2024, EFSA (2024) published a reasoned opinion on the MRLs for difenoconazole. It also proposed a new residue definition for "difenoconazole – alcohol (CGA205375), expressed as difenoconazole" applicable to animal products, based on the results of studies on difenoconazole residues in livestock.
In October 2024, the EU raised the MRL for difenoconazole on rye and wheat from 0.1 to 0.3 mg/kg following an application to modify MRLs on these crops, based on EFSA’s (2023) conclusion that the modifications were acceptable for consumer safety.
A minor correction to Regulation 2024/2612 was published in February 2025.
MRLs are set in accordance with the rules set out in Regulation 396/2005. For information on current MRLs for other substances, please consult the EU Pesticide Residues database.
Timeline
This Regulation is under discussion and is expected to be adopted in 2026.
Background
MRLs are set in accordance with the rules set out in Regulation 396/2005. For information on current MRLs for other substances, please consult the EU Pesticide Residues database.
Resources
EFSA (2023) Modification of the existing maximum residue levels for difenoconazole in wheat and rye. EFSA Journal, 21(8): 8207.
EFSA (2024) Review of the existing maximum residue levels for difenoconazole according to Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No396/2005. EFSA Journal, 22: e8987.
EFSA (2025) Setting of import tolerances for difenoconazole in various crops. EFSA Journal, 23: e9472.
Regulation (EU) 2024/2612 as regards maximum residue levels for chitosan, clopyralid, difenoconazole, fat distillation residues, flonicamid, hydrolysed proteins, and lavandulyl senecioate in or on certain products, and Corrigendum.
Sources
Draft Commission Regulation as regards maximum residue levels for difenoconazole in or on certain products [download]
Draft Annex II [download]
Tables & Figures
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.
EU discusses MRLs and import tolerances for difenoconazole on various products
Draft Commission Regulation as regards maximum residue levels for difenoconazole in or on certain products [download]
Draft Annex II [download]
What is changing and why?
The European Union (EU) is discussing new maximum residue levels (MRLs) for difenoconazole, summarised in Table 1. This includes lowering the MRLs to the to the limit of determination (LOD, the lowest level that can be detected using the most modern and reliable analytical methods) for certain products where information from the European Food Safety Authority was not sufficient to rule out risks for consumers. These are highlighted in Table 1.
For citrus fruits, tree nuts, mangoes, papayas, dry peas, and soyabeans, where proposed MRLs are not considered to be a concern for consumer safety, import tolerances are being discussed.
Timeline
This Regulation is under discussion and is expected to be adopted in 2026.
Tables & Figures
Disclaimer: Under no circumstances shall COLEAD be liable for any loss, damage, liability or expense incurred or suffered that is claimed to have resulted from the use of information available on this website or any link to external sites. The use of the website is at the user’s sole risk and responsibility. This information platform was created and maintained with the financial support of the European Union. Its contents do not, however, reflect the views of the European Union.